X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 16,731 times.
Learn more...
Every wanted to save data, and load them again every time a player enters the game again? Ever since Data Persistence has become futile, ROBLOX introduces data stores that are much more functioning. The following how-to-guide will enable you to work with datastores for ROBLOX.
Steps
Method 1
Method 1 of 3:
Setting the Data Store
-
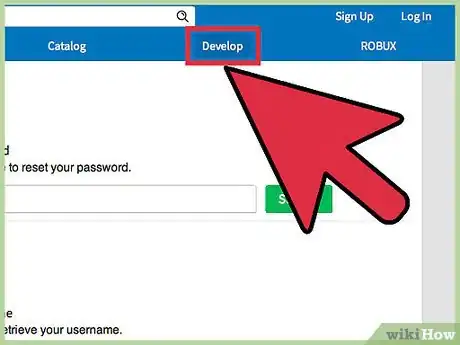
1Configure the API. This does not involve any bit of scripting, but in order to activate all of the data store API, you must first enable the API access. To do this, go to the Develop tab, and click on "Games". This should direct you to all of the current game places you own. Find your game, and click on the gear. There should appear a dropdown menu, and simply press "Configure". Check the box enabled "Enable Studio Access to API Services", and save. You should now have access to the complete API.
-
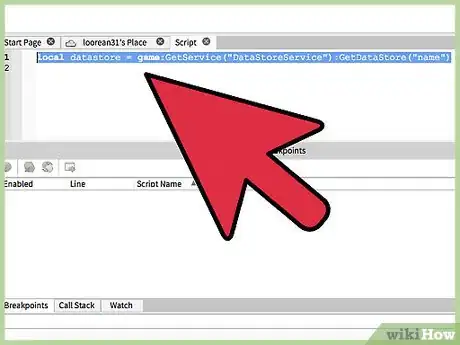
2Retrieve the data store. Use the Data Store API to call for the data store, as we will need to reference it. To start, open a script on ROBLOX, and name a variable that we would like to use to call for the reference.
local datastore = game:GetService("DataStoreService"):GetDataStore("name")
Advertisement -
3Use the variable as needed. You've successfully called the datastore with the variable "datastore". Now, whenever you need to retrieve the datastore, you can simply name it by its variable.
- Please note that if a data store has not been created yet, it will automatically create a new one.
Advertisement
Method 2
Method 2 of 3:
Using Data Store Methods
-
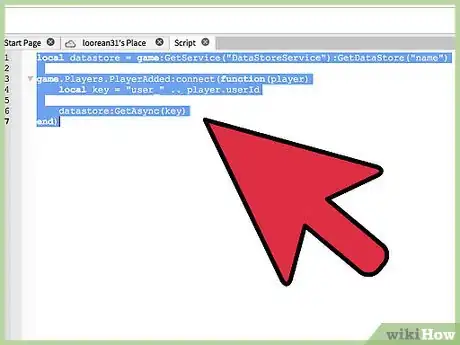
1GetAsync. Use GetAsync to return the value of the entry in the data store with the given key. Make sure to give each player a unique set of keys, as setting two players the same key will override their own in-game data, causing chaos between the two parties. If you want to know how to set a unique key, read on.
- The following code will output nil, because the server couldn't find any value linking to the key; it is important to show the server exactly what we are trying to output, so that the server will know what needs to be displayed.
local datastore = game:GetService("DataStoreService"):GetDataStore("name") game.Players.PlayerAdded:connect(function(player) local key = "user_" .. player.userId datastore:GetAsync(key) end)
-
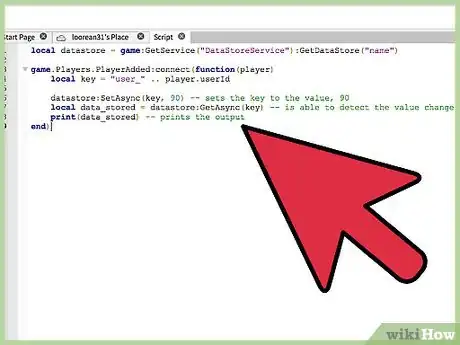
2SetAsync. Use SetAsync to set the value of the key, and overrides all existing data stored for the unique key.
- If the previous set of information is important, consider using UpdateAsync, which will be taught below.
- The following code shows you how to implement both, the ":GetAsync()", and the ":SetAsync()", methods.
- Note: This will not work, unless you have the API access enabled. To do this, read the first instruction of this guide.
local datastore = game:GetService("DataStoreService"):GetDataStore("name") game.Players.PlayerAdded:connect(function(player) local key = "user_" .. player.userId datastore:SetAsync(key, 90) -- sets the key to the value, 90 local data_stored = datastore:GetAsync(key) -- is able to detect the value change print(data_stored) -- prints the output end)
-
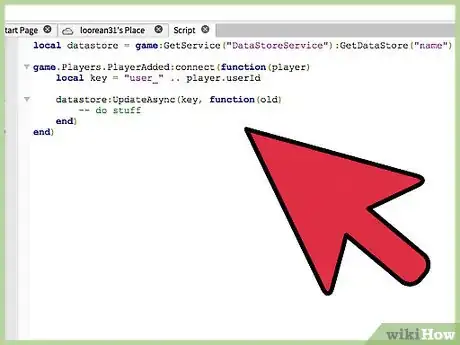
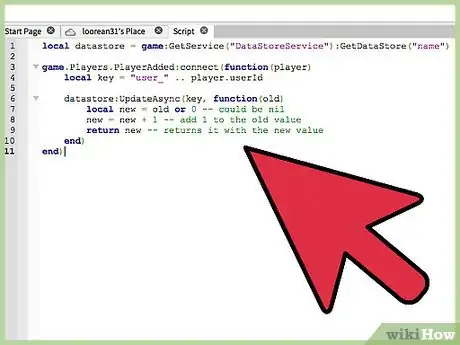
3Use UpdateAsync to return the value of the key, and updates it with a new value. This validates data, and must therefore wait until the server can find the time to update it. For this to work, you will need to pass two parameters; the first is a string that takes the unique key you have set up: "'user_' .. player.userId", and the second is a function that will take in the old value.
- In this case, we called the old value "old". Inside this function, we will need to make a variable that will account for our updated score, and then return that so it can display our new score.
- Note that the server will return nil if the key does not exist or is not assigned correctly.
- If the function does not exist, the update will be cancelled.
local datastore = game:GetService("DataStoreService"):GetDataStore("name") game.Players.PlayerAdded:connect(function(player) local key = "user_" .. player.userId datastore:UpdateAsync(key, function(old) -- do stuff end) end)
local datastore = game:GetService("DataStoreService"):GetDataStore("name") game.Players.PlayerAdded:connect(function(player) local key = "user_" .. player.userId datastore:UpdateAsync(key, function(old) local new = old or 0 -- could be nil new = new + 1 -- add 1 to the old value return new -- returns it with the new value end) end)
-
4Use IncrementAsync to increment the value for a key, and returns the incremented value. This method only works on integers.
Advertisement
Method 3
Method 3 of 3:
Data Store Events and Updating Data
-
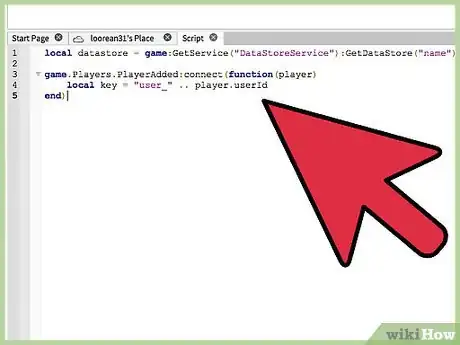
1Set a unique key. It is extremely vital that every player has a key that is unique to them. They will hold onto that key, which will store all of their data. In order to do this, we use the player's ID. Once you have set the data store, simply call on a function to load the player, and then find the player's ID. The code should look as follows:
- This will automatically create a key that is unique to that player only, for every player will have one unique ID. The "user_" will not matter.
local datastore = game:GetService("DataStoreService"):GetDataStore("name") game.Players.PlayerAdded:connect(function(player) local key = "user_" .. player.userId end)
-
2Update the data. Now that you've got a unique key to each player, you're set to making the data store update and retrieve data. Underneath your key, you will want to add a method that is most suitable to your needs. In this case, we'll use "UpdateAsync".
- Start with a function to help the server understand what you are intending to do.
- In this function, we set up another function, old. "old" was our previously saved data. In this scenario, every time a player entered the server, the server would locate its key, which is their userId, and it would update the data by 50 points, returning and displaying that new value.
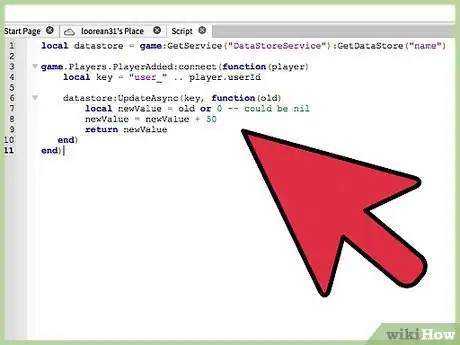
local datastore = game:GetService("DataStoreService"):GetDataStore("name") game.Players.PlayerAdded:connect(function(player) local key = "user_" .. player.userId datastore:UpdateAsync(key, function(old) local newValue = old or 0 -- could be nil newValue = newValue + 50 return newValue end) end)
-
3Congratulations! You've successfully stored and updated a player's data.
Advertisement
Warnings
- When first creating your data store, make sure to have "game:GetService("DataStoreService")", with the correct capitalization. It will not run efficiently, if it is called incorrectly.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Make sure to know when to use "SetAsync" and "UpdateAsync", as using the wrong one can turn things into a mess when retrieving data. In most cases, developers will use "UpdateAsync".⧼thumbs_response⧽
Advertisement
About This Article
Advertisement