This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff. Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards.
There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 85% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 190,358 times.
Learn more...
Dams are structures designed to stop, restrict, or control the flow of water. They're often constructed in rivers in order to redirect the water for other purposes, such as farming or industrial use. Large rivers are usually dammed by teams of engineers, who must carefully calculate the size and shape of the structures to ensure that they're able to withstand the pressure of the water. However, it's possible to dam up a small river using natural materials like rocks, sticks, and mud.
Steps
Laying the Foundation
-
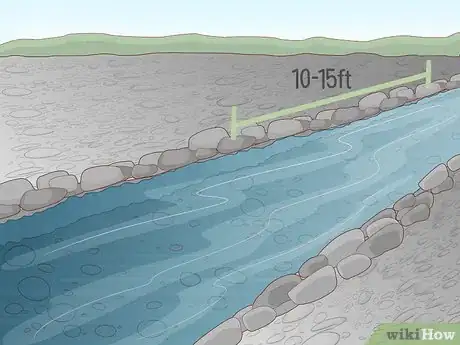
1Designate a shallow, manageable section of the river as the site for your dam. It will take less time to create a barrier across narrow sections, but they're also where the water typically flows the fastest. Conversely, wider sections tend to be more calm, but blocking them off may require quite a bit more material and labor. If possible, try to find a site that offers a good compromise between size and ease of access.[1]
- Be sure to also take into account how much time you have, as well as the amount of raw materials available to you. For instance, you may be able to dam up a 10–15 ft (3.0–4.6 m) section of the river in a just few hours using materials gathered on-site.
- Avoid areas where the river floor is especially soft, loose, or uneven. A weak base could leave your dam vulnerable to leakage. If the floor of the section you've chosen for your dam is too deep for you to see or feel, it's probably too deep to build on.
-
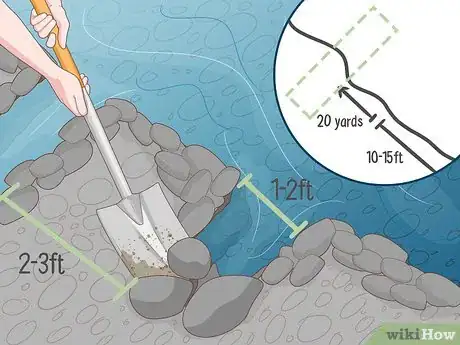
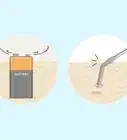
2Dig one or more trenches upstream of the dam site to divert the river. Pick a point 10–20 yards (9.1–18.3 m) above the section of river you've selected for your dam. Use a shovel, drainage spade, or trenching hoe to remove the dirt or sand along the riverbank in long, straight pits roughly 1–2 ft (0.30–0.61 m) wide. If you do this correctly, your trenches will drain the water from the river's main channel, allowing you to begin constructing your dam.
- If you're digging multiple trenches, space them about 2–3 ft (0.61–0.91 m) apart to prevent the trapped water from draining back into the river. Angle each of your trenches away from the river in the same direction, parallel to one another.
- Make sure you dig your trench or trenches deep enough to carry the water away from the river without creating surface runoff.
- It's not necessary to empty the river completely. You just need to direct enough water out of the main channel to make it sufficiently shallow to work in.
Tip: The larger the river, the more trenches you'll need to dig in order to effectively divert the flow of water.
Advertisement -
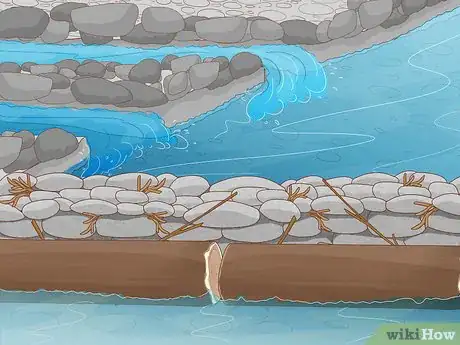
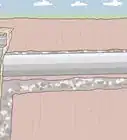
3Lay rocks across the riverbed to serve as the foundation for your dam. Put the biggest, heaviest rocks down first, then stack increasingly-smaller rocks on top. Hand-pick stones of various sizes to plug any significant gaps in the stack.[2]
- Flat rocks with squared edges will work best, as they offer a tighter fit and leave fewer openings than rocks with rounded edges.
- The foundation for your dam can be anywhere from 1-5 rocks wide, depending on its intended size.
Assembling the Main Structure
-
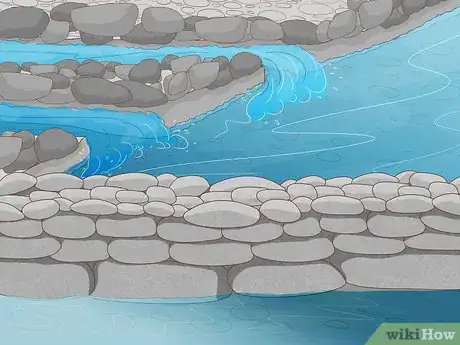
1Pile on sticks until your dam reaches the desired height. Build up the main structure of your dam on both sides of your foundation. As you did when setting the rocks, place the heaviest items on the bottom to provide a sturdier base, then layer smaller pieces on top.
- Wedging your bottom layer of sticks under your rock foundation will keep them from being swept away once you resume the flow of water.
- Similarly, crossing the sticks on top (the way you would when building a fire) will increase their structural strength.
-
2Reinforce the downstream side of your dam with logs or tree limbs. This will prevent your other materials from shifting or collapsing under the force of the water. Arrange the timber so that it completely spans both banks of the river. If possible, anchor the ends of your supports deep in the mud of the riverbed.[3]
- Fallen trees can be perfect for bracing your foundation, if you can manage to transport them to the dam site.
- You can also use pressure-treated lumber or pieces of scrap wood for this purpose.[4]
Tip: For maximum stability, push 2 rows of logs, tree trunks, or thick branches together so that they sit flush against one another and situate a third row of materials in the crevice where the bottom rows meet.
-
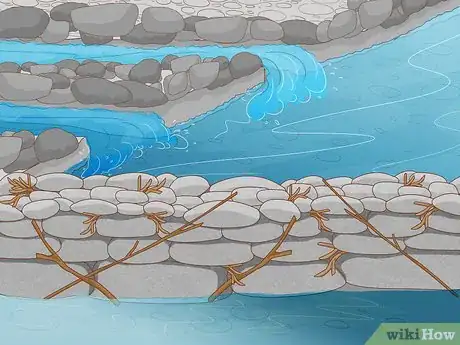
3Use twigs, leaves, or mud to seal the gaps in your dam. Stuff handfuls of brush into any openings where flowing water might find its way through. Try to compact your filler material as much as possible. Ideally, you want to stem even the slightest trickle.
- This is often the most time-consuming part of building a dam, as there will be lots of small holes to fill.
- If you only want to limit the amount of water that passes through the river's main channel, feel free to skip this step.
Completing Your Dam
-
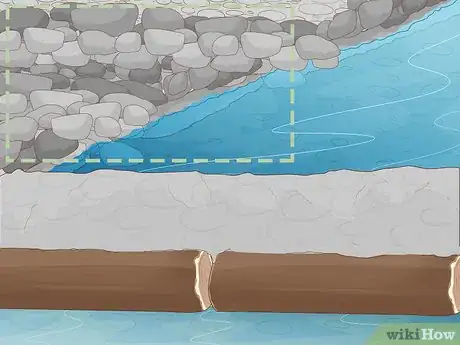
1Cover the dam with mud to secure your materials. Shovel the mud onto the dam starting from the bottom and working your way towards the top. Once the entire structure is covered, pack the mud down tight using the blade of your shovel or the palms of your hand to make sure it doesn't wash away.
- Clay-type muds make the best covering, if they're available—they're denser and stickier than ordinary mud and bake to a hard shell under the heat of the sun.[5]
Tip: Avoid mud filled with sand, rocks, wood fragments, and similar debris. Loose materials may affect the consistency of the mud, making it harder to pack and more likely to crumble.
-
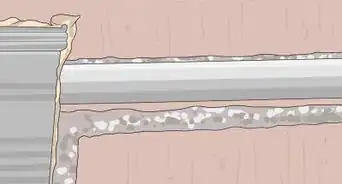
2Concrete your dam to make it a permanent addition to the river. If you want your dam to block or divert water for more than a short time, you'll need longer-lasting materials than rocks and stick. Mix a bag of quick-setting concrete mix with water in a large bucket or wheelbarrow and pour the wet concrete into the cracks. Once the concrete dries, it will continue holding back the water well into the future.[6]
- Allow the concrete to cure for 5-7 days before restoring the flow of water to the river. Curing takes place when concrete is given time to dry to its full hardness.[7]
- You have the option of either pouring concrete immediately after putting down your foundation (if you think it's tall enough on its own) or waiting until you've got your other materials in place and cementing the entire dam.
-
3Fill the diversion trenches to redirect the water back into the river. Pile earth, stones, and other materials over the mouth of each trench to close it off. If you dug multiple trenches, wait a few minutes for the water level to stabilize behind the dam before moving onto the next. Proceed in this way until you've closed every last one.
- It doesn't matter which order you close the trenches in—with each one, more water will make its way back into the river's main channel until it's following its natural course once again.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionWhat materials are the strongest for this purpose?
 Community AnswerVery large boulders for most of the dam, and pack a lot of dirt on top of that. If you really want the dam to be waterproof, then you can lay a sheet of tarp on top of the dam.
Community AnswerVery large boulders for most of the dam, and pack a lot of dirt on top of that. If you really want the dam to be waterproof, then you can lay a sheet of tarp on top of the dam. -
QuestionWhen damming a small creek, how do I keep the sides from blowing out and the creek going around the dam?
 Community AnswerYou should dig out a big reservoir and then build a wall surrounding the reservoir.
Community AnswerYou should dig out a big reservoir and then build a wall surrounding the reservoir. -
QuestionWhen building a dam across a river, how far on each side of the dam does it go in the earth?
 Uni stormCommunity AnswerIf your dam is going to build up large amounts of pressure, then far into the walls. But at the same time, if your river bed and walls are made rock or hard clay/mud, then the sides would not have to go very far in. The best idea would be about 1 foot to half a foot (a couple of centimeters).
Uni stormCommunity AnswerIf your dam is going to build up large amounts of pressure, then far into the walls. But at the same time, if your river bed and walls are made rock or hard clay/mud, then the sides would not have to go very far in. The best idea would be about 1 foot to half a foot (a couple of centimeters).
Warnings
- While dams can be useful for short-term projects like construction or irrigation, they're ultimately damaging to the rivers they're built in. When left in place, dams can disrupt the natural movement of water, destroying habitats and endangering wildlife in the process.[8]⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You'll Need
Laying the Foundation
- Shovel
- Rocks
Assembling the Main Structure
- Sticks
- Logs or tree limbs
- Twigs, leaves, and mud
- Pressure-treated lumber or scrap wood (optional)
Completing Your Dam
- Shovel
- Mud
- Quick-setting concrete mix, water, and bucket (optional)
References
- ↑ https://wikiwater.fr/e7-construction-of-small-surface
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lBKs2NliDzw&feature=youtu.be&t=5
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wj7ZCMjF_aQ&feature=youtu.be&t=235
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XVpivmMO6xk&feature=youtu.be&t=230
- ↑ https://uwsslec.libguides.com/c.php?g=186890&p=1236569
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KFL-Bp6YNAU&feature=youtu.be&t=262
- ↑ https://www.quikrete.com/pdfs/data_sheet-concrete%20mix%201101.pdf
- ↑ https://www.americanrivers.org/threats-solutions/restoring-damaged-rivers/how-dams-damage-rivers/
About This Article
With the right materials and some heavy lifting, you can dam a river yourself. Choose a shallow, narrow section of the river to dam. Dig a few trenches 10 to 20 yards upstream of your dam location to divert the river. Then, lay logs, big branches, rocks, and sticks to build your dam. To protect the materials, cover them with mud, or concrete if you want the dam to be permanent. If any water is coming through the dam, plug the gaps with twigs, leaves, and more mud. Once you’ve finished your dam, block off the trenches you dug with smaller dams to keep the water in the river. For more tips, including how to cure a concrete dam, read on!