This article was co-authored by Siddharth Tambar, MD. Dr. Siddharth Tambar, MD is a board certified rheumatologist at Chicago Arthritis and Regenerative Medicine in Chicago, Illinois. With over 19 years of experience, Dr. Tambar specializes in Regenerative Medicine and Rheumatology, with a focus on platelet rich plasma and bone marrow derived stem cell treatments for arthritis, tendinitis, injuries, and back pain. Dr. Tambar holds a BA in Economics from State University of New York at Buffalo. He earned his MD from State University of New York at Syracuse. He completed his Internship, Residency in Internal Medicine, and his Rheumatology Fellowship at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. Dr Tambar is board certified in both rheumatology and internal medicine. He also holds Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Diagnostic and Interventional certifications from the American College of Rheumatology and the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine.
There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 25,497 times.
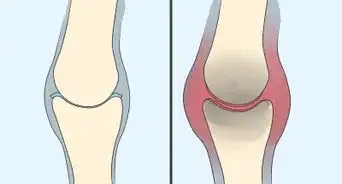
Septic arthritis, or infectious arthritis, is an infection of a joint space caused by bacteria or a virus.[1] It usually develops in only one joint following surgery, so orthopedic surgeons are always on the lookout for signs of this condition. Septic arthritis is most common in large joints like the hip, knee or shoulder. Any person can develop septic arthritis. However, some individuals such as drug users, children, or those with lupus or gout are more susceptible to the disorder. A doctor can definitively diagnose septic arthritis and related joint damage through an exam and possible testing. From this, your doctor can develop a plan to address the infection, which may include antibiotics and surgery. You can treat septic arthritis by receiving medical treatment and using self-care to ease it.
Steps
Receiving Medical Treatment
-
1Heal viral septic arthritis without medication. Your doctor may diagnose the cause of your septic arthritis as a virus. Most cases of viral septic arthritis won’t require any antibiotics. Instead, your doctor may allow the infection to heal on its own and/ or ease pain and swelling with drainage.[2]
- Recognize that you may need surgery to treat tissue damage even if the infection heals on its own.
- Viral etiologies of septic arthritis are rare, while bacterial infection is quite common.
-
2Take an antibiotic. If bacteria are the cause of your septic arthritis, your doctor will likely prescribe an antibiotic.[3] Risk factors include diabetes, increasing age, rheumatoid arthritis, joint replacement, recent surgery, skin infection, alcoholism, IV drug use, and articular corticosteroid injection. You may need oral antibiotics or an intravenous injection. Antibiotics generally stop the infection within a few days or weeks.[4]
- Be aware that if you have a severe case of septic arthritis, you may require a long course of antibiotic treatment.
- Ask your doctor about any side effects your prescribed antibiotic may have. Side effects include: nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.[5]
- Diarrhea could be a sign of C. Difficile Colitis (C. Diff.), an infection of the colon caused by antibiotic use.
- Take the entire course of your prescribed antibiotic, even if you are feeling better. This can minimize the risk of the infection getting worse or coming back.
Advertisement -
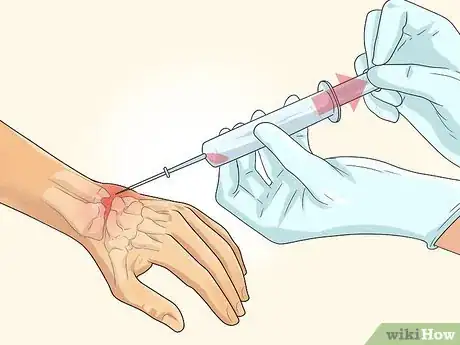
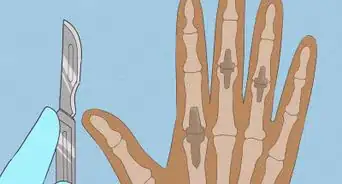
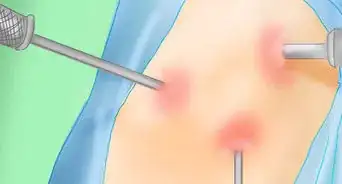
3Undergo fluid withdrawal.[6] Another common medical treatment for septic arthritis is removing infected fluid from the joint. This is also called synovial fluid drainage. Withdrawal not only drains infected fluid, but can also ease pain and swelling and prevent further damage to your joint. Your doctor may remove fluid by:[7]
- Needle aspiration, or arthrocentesis, is a bedside procedure in which your doctor drains/taps the infected fluid by inserting a needle into the joint space.
- Arthroscopy, in which your doctor inserts a flexible tube with a video camera into your joint through a small incision. The doctor then inserts suction and drainage tubes to remove the fluid. Your doctor may leave the tubes in your joint for a few days to get rid of all of the fluid.
- Open surgery, which a doctor usually performs for severe infections or those in large joints such as the hip.[8] Surgery can wash out the infected joint and may also remove any damaged sections. This treatment is common in patients with infection from an artificial joint replacement.
-
4Consider physical therapy once healing begins. Your doctor may suggest physical therapy once your septic arthritis begins to heal. Physical therapy is often used to treat severe septic arthritis with joint damage. It can help you regain mobility, improve your range of motion, and build muscle to prevent further damage to your joint.[9]
- Talk to your doctor about physical therapy to ease your septic arthritis. Your doctor can let you know if it’s appropriate for your case and may suggest a specific therapist for you.[10]
Using Self-Care to Ease Septic Arthritis
-
1Take an anti-inflammatory pain reliever. Septic arthritis is often painful. It may also cause swelling or inflammation at your joint even after having fluid withdrawn. Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDS, can ease your pain and any inflammation. You can use an over the counter NSAID or have your doctor prescribe one for more serious pain.[11]
- Select an NSAID such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve), and celecoxib (Celebrex).
- Follow the dosing instructions your doctor provides. If your doctor doesn’t suggest guidelines for taking the medication, follow the instructions on the product label.
-
2Rest the joint. Your doctor will likely prescribe rest to treat your septic arthritis. This includes not moving the joint or surrounding area as much as possible. In some cases, your doctor may splint your arm to provide it more rest.[12] Rest is the first part of a commonly used treatment that is known as RICE. RICE stands for:
- R= REST
- I= ICE
- C= Compression
- E= Elevation
-
3Raise the joint. Your joint may continue to swell even after fluid withdrawal. If this happens, raise the joint above your heart.[13] This can aid drainage of the fluid and reduce swelling. It may also ease pain.
- Use a wedge, pillows or other props to raise the affected joint above your heart.
-
4Protect the joint. In addition to resting and raising your joint, it’s also important to protect it from further injury or damage. This includes taking all of your prescribed medications. You should also do avoid knocking or bumping the joint against anything as this may cause further pain, swelling, or injury.[14]
- Leave on splinting until your doctor instructs you to remove it. Splints can protect the joint and remind you to not hit it on anything.
-
5Apply a cool compress. Pain and swelling are typical symptoms of septic arthritis and may linger even as you begin to heal. Putting a cool or cold compress on the affected joint can reduce swelling and relieve any pain or discomfort you have.[15]
- Use ice or a cool washcloth as a compress.
- Apply your cool compress for 20 minutes at a time as often as you need it.[16]
- Wrap an ice pack or bag of frozen peas or corn in cloth to protect your skin from getting numb. If this happens, remove the pack.
-
6Exercise once healing begins. If you are taking an antibiotic and/or underwent fluid drainage as well as rested your joint, you may start to feel better within a few days. As you feel better, try gentle and low-impact exercise. This can help speed your recovery.[17]
- Ask your doctor if you are healthy enough to exercise, even if it is light. Your doctor may suggest physical therapy instead of exercise in some cases.
- Choose a low impact type of exercise such as walking or swimming. Things such as bicycling may be too much, especially if your septic arthritis is in the knee or hip.
- Always follow the instructions of your doctor and physical therapist and do not push yourself too hard without asking and getting their approval first. Know your limits!
Expert Q&A
-
QuestionCan I treat septic arthritis at home?
 Siddharth Tambar, MDDr. Siddharth Tambar, MD is a board certified rheumatologist at Chicago Arthritis and Regenerative Medicine in Chicago, Illinois. With over 19 years of experience, Dr. Tambar specializes in Regenerative Medicine and Rheumatology, with a focus on platelet rich plasma and bone marrow derived stem cell treatments for arthritis, tendinitis, injuries, and back pain. Dr. Tambar holds a BA in Economics from State University of New York at Buffalo. He earned his MD from State University of New York at Syracuse. He completed his Internship, Residency in Internal Medicine, and his Rheumatology Fellowship at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. Dr Tambar is board certified in both rheumatology and internal medicine. He also holds Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Diagnostic and Interventional certifications from the American College of Rheumatology and the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine.
Siddharth Tambar, MDDr. Siddharth Tambar, MD is a board certified rheumatologist at Chicago Arthritis and Regenerative Medicine in Chicago, Illinois. With over 19 years of experience, Dr. Tambar specializes in Regenerative Medicine and Rheumatology, with a focus on platelet rich plasma and bone marrow derived stem cell treatments for arthritis, tendinitis, injuries, and back pain. Dr. Tambar holds a BA in Economics from State University of New York at Buffalo. He earned his MD from State University of New York at Syracuse. He completed his Internship, Residency in Internal Medicine, and his Rheumatology Fellowship at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. Dr Tambar is board certified in both rheumatology and internal medicine. He also holds Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Diagnostic and Interventional certifications from the American College of Rheumatology and the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine.
Board Certified Rheumatologist You can use home remedies to alleviate your symptoms, but you'll likely need antibiotics or a fluid removal procedure to beat the infection. Talk to your doctor to find out which treatment will work best for you.
You can use home remedies to alleviate your symptoms, but you'll likely need antibiotics or a fluid removal procedure to beat the infection. Talk to your doctor to find out which treatment will work best for you.
References
- ↑ Siddharth Tambar, MD. Board Certified Rheumatologist. Expert Interview. 25 August 2020.
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bone-and-joint-infections/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350760
- ↑ Siddharth Tambar, MD. Board Certified Rheumatologist. Expert Interview. 25 August 2020.
- ↑ http://www.arthritis.org/about-arthritis/types/infectious-arthritis/
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bone-and-joint-infections/diagnosis-treatment/treatment/txc-20166672
- ↑ Siddharth Tambar, MD. Board Certified Rheumatologist. Expert Interview. 25 August 2020.
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bone-and-joint-infections/diagnosis-treatment/treatment/txc-20166672
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bone-and-joint-infections/diagnosis-treatment/treatment/txc-20166672
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/septic-arthritis/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC126863/
- ↑ https://www.drugs.com/cg/septic-arthritis.html
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000430.htm
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000430.htm
- ↑ http://www.arthritis.org/about-arthritis/types/infectious-arthritis/
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000430.htm
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-fractures/basics/art-20056641
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000430.htm









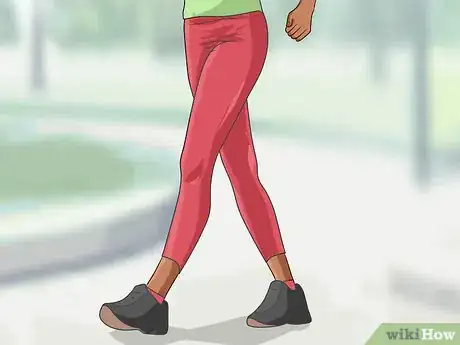







































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...