This article was written by Stan Kats and by wikiHow staff writer, Nicole Levine, MFA. Stan Kats is the COO and Chief Technologist for The STG IT Consulting Group in West Hollywood, California. Stan provides comprehensive technology & cybersecurity solutions to businesses through managed IT services, and for individuals through his consumer service business, Stan's Tech Garage. Stan has over 7 years of cybersecurity experience, holding senior positions in information security at General Motors, AIG, and Aramark over his career. Stan received a BA in International Relations from The University of Southern California.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article's instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 19,355 times.
Did you accidentally delete an irreplaceable file from your Windows 10 PC? It happens to the best of us! Fortunately, there are many safeguards in place that make it easy to recover your files before they are gone forever. This wikiHow article will show you how to undelete files using free tools built into Windows and two other easy data recovery tools.
Steps
Checking the Recycle Bin
-
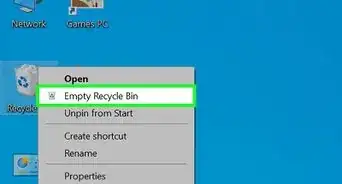
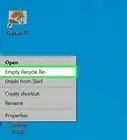
1Open the Recycle Bin on your PC. Before you panic or try another method, double-check your Recycle Bin to make sure the file isn't still in there. You'll usually see the Recycle Bin icon on your desktop, but if you don't, you can also fine it by pressing the Windows key, typing recycle, and clicking Recycle Bin.
-
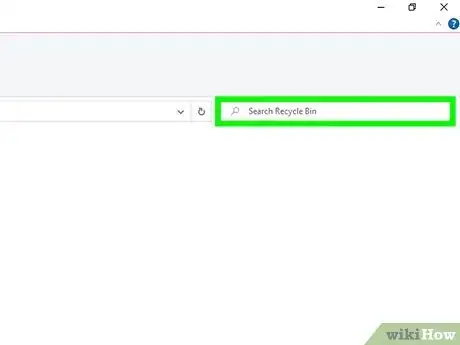
2Browse or search for a file. If your Recycle Bin has a lot of files, it may be helpful to use the search bar at the top-right corner. You can also simply scroll through the files to look for the one you need.Advertisement
-
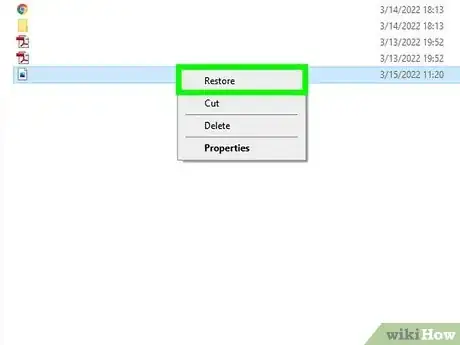
3Right-click a file and choose Restore. This will return the deleted file to the folder from which you deleted it.
- To restore multiple files at once, hold down the Control key as you click each file, then right-click anywhere in the highlighted area and choose Restore.
- You can also restore all deleted files from the Recycle Bin at once by clicking Restore all items at the top of the window.
Using Windows File Recovery
-
1Know when to use this method. If you aren't able to restore a file from the Recycle Bin or find it in your backup, this method can help you regain access to lost files.[1]
- You have to restore the missing files to a drive that is not the same drive the file was deleted from—this means that if you only have one hard drive, you'll need to connect a USB flash or other external drive to your PC to restore the lost files. If you don't have another drive to use, you won't be able to use this method.
- It's not possible to restore files to or from a cloud storage or networked drive with this method.
-
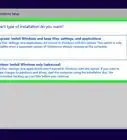
2Install Windows File Recovery by Microsoft. This utility might already be installed on some systems, but not all.
- Open the Microsoft Store app from the Windows Start menu.
- Search for Windows File Recovery.
- If you see the option to do so, click Get and follow the on-screen instructions to install.
- If the app is already installed, you'll see Open instead.
-
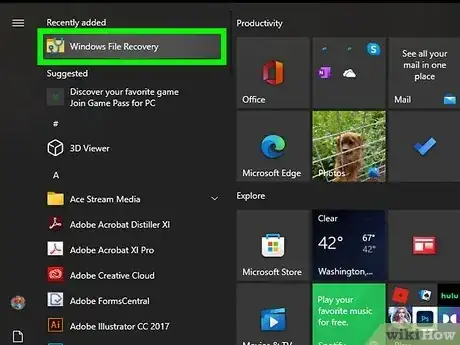
3Open Windows File Recovery. It's easy—just type windows file recovery into the Windows Search field (press Windows key + S if you don't see it), and then click Windows File Recovery in the search results. This will open a command prompt window.
- If prompted, give the app permission to make changes to your computer.
-
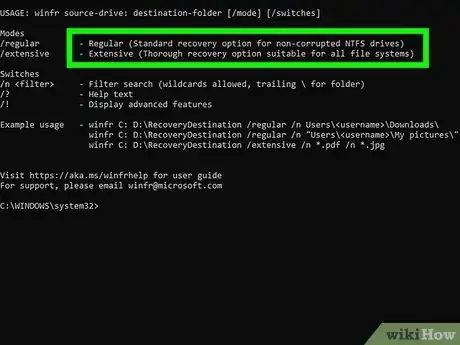
4Determine the mode you want to use. There are two different modes for restoring files:
- Regular mode: Use this mode if the file you deleted was from a drive formatted with NTFS and the drive is not corrupted.
-
Extensive mode: Use this mode if the file you deleted was on a drive formatted as FAT or exFAT, which is common for flash cards and other removable media, or the drive is corrupted. This mode will take a little longer.
- If you're not sure which mode to use, start with Regular mode, and then try Extensive if that doesn't work.
-
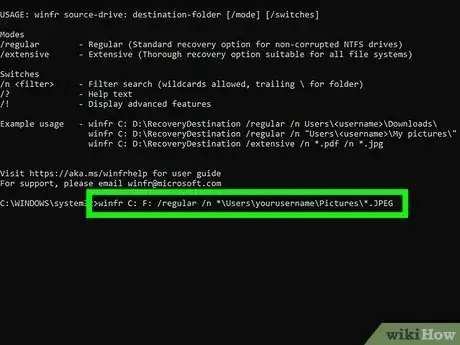
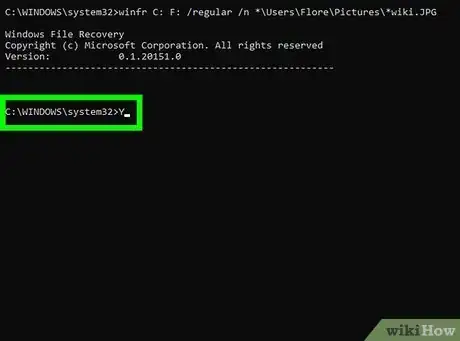
5Use the winfr command to restore your files. The command will look like this winfr source-drive: destination-drive: /mode /switches file-or-folder. The /n switch lets you specify files and folders to recover. Here are some examples you can use in both regular and extensive modes:
- If you want to recover all files ending with .JPEG from your pictures directory on the C drive to a recovery folder on your F drive, you'd use winfr C: F: /regular /n *\Users\yourusername\Pictures\*.JPEG.
- You can also use /n multiple times to recover files that meet multiple criteria. For example, to recover both JPEG and PNG files from your Pictures folder, you could use winfr C: F: /regular /n \Users\yourusername\Pictures\*.JPEG /n \Users\yourusername\Pictures\*.PNG.
- To recover all files ending with .docx from any location on the original drive, you could use winfr C: F: /regular /n *.docx.
- To recover your entire Documents folder from the C: drive to the F: drive, you'd use winfr C: F: /regular \Users\yourusername\Documents\.
- Note the trailing backslash \ at the end of the folder name—this is necessary when recovering an entire folder.
-
6Press Y to confirm. Windows File Recovery will now attempt to recover the file(s). If the recover is successful, the files will be saved to the destination drive in a new folder called "Recovery_(date and time).
- If you're unable to recover the files in regular mode, run the same command again replacing /regular with /extensive.
- Some file types are hidden from results by default, including .log, .vbs, .c, .cab, .py, and .lnk. If you are unable to find the type of file you're looking for, run the recovery again, this time adding the /e switch to disable extended filtering.
Restoring from File History
-
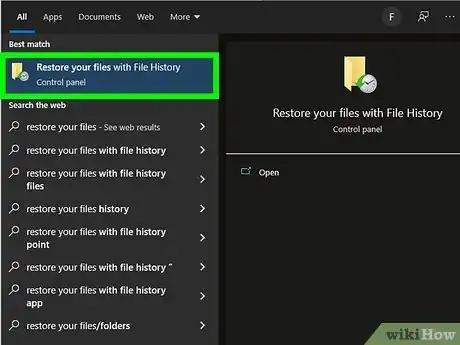
1Open the File History tool. If you want to recover a file or folder you've accidentally overwritten or replaced with a newer version in your Documents, Music, Pictures, Videos, or Desktop folder, this method will help you get your original file(s) back. To open the tool, press the Windows key on your keyboard, type restore your files, and then click Restore your files with File History.[2]
- This method requires that you've enabled File History in your settings. File History works with a network or external drive, so if you don't have one of those, you don't have File History enabled.[3]
- If the file you want to recover no longer exists at all, you can restore its containing folder to a previous version that existed before you deleted the file.
-
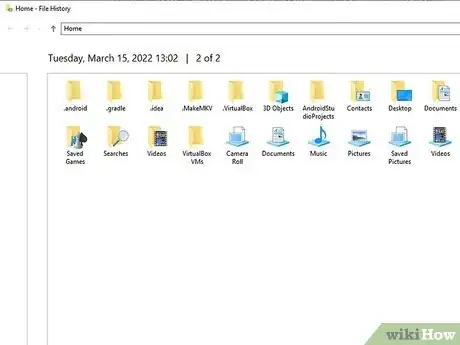
2Locate the file or folder you need in the File History tool. All of the files that have earlier versions saved will be visible here. Once you find the file, you'll be able to browse the dates of previously saved versions.
-
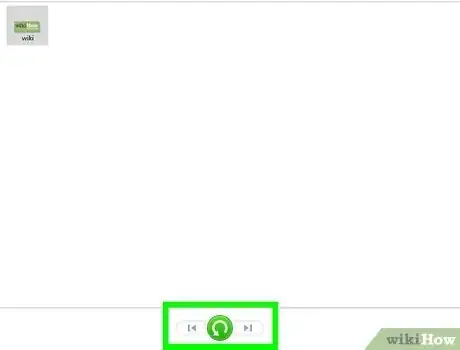
3Use the arrows to select the version to restore. Be sure to choose a version of the file or folder that existed before you made the change.
-
4Select a version and click Restore. A confirmation message will appear.
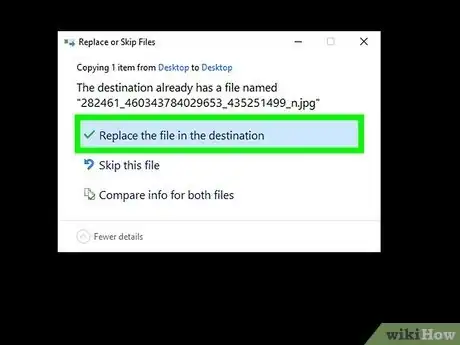
- If you'd rather restore the file or folder to a different location, right-click Restore, choose Restore to, and then click another location.
-
5Click Restore to confirm. This saves the original version of the file or folder to its original location.
Using Recuva (Free)
-
1Install Recuva. Recuva is a free app that will undelete files you accidentally removed from your computer.[4] You can get the tool from https://www.ccleaner.com/recuva.
- The free version of the tool should be enough for recovering most deleted files.
-
2Open Recuva once installed. You'll find it in your Windows menu. If prompted, allow the app to make changes to your PC.
- The first time you open Recuva, you may see a warning message about the app being blocked. Click the warning message, select the first option in the list, select the Actions menu, and then click Allow on device to continue.
-
3Click Next on the wizard. Now you'll be able to use this quick-start feature to recover deleted files.
-
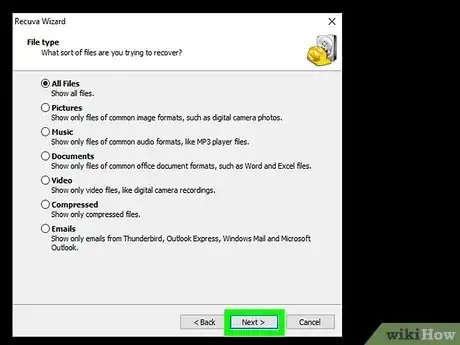
4Select a file type and click Next. If you're not sure the type of file you're looking for, choose All Files.
-
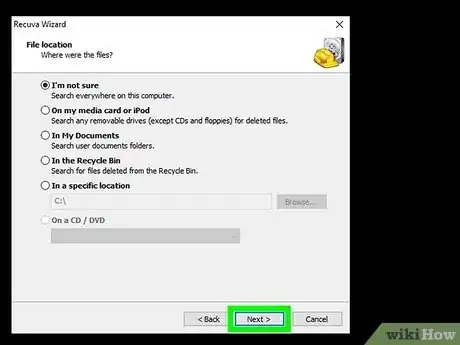
5Select the location the file was deleted from. For example, if you deleted the file from Recycle Bin, choose In the Recycle Bin.
- To enter a specific folder, choose In a specific location, click Browse…, and then select the folder.
-
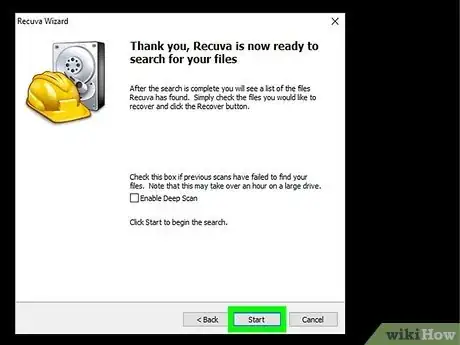
6Click Next. Recuva will now attempt to find deleted files.
- You'll see that there's a Deep Scan option here. Try the regular scan first. If you are unable to recover your file normally, you can close and re-open Recuva and check the box next to "Enable Deep Scan." This option will take a long time, and it might not be necessary.
-
7Click Start. Recuva will now search for shadow copies of deleted files from the selected location. Once the scan is complete, a list of files will appear.
-
8Select the file(s) you want to recover and click Recover…. This restores the selected file(s) and/or folder(s) to the original location.
Restoring from an Older Backup
-
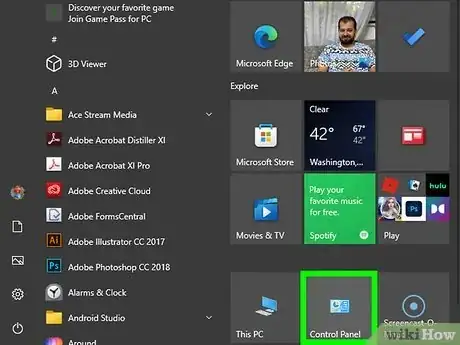
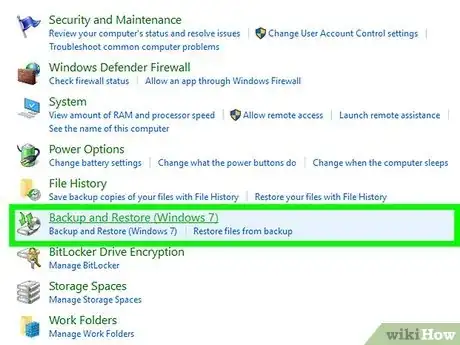
1Open the Control Panel. If you back up your PC to another drive, including a networked drive, or another version of Windows that was installed on your PC, you can restore files at any time from earlier backups. To get started, press the Windows key and type control panel, then click Control Panel in the search results.[5]
-
2Open the Backup and Restore tool. If you don't see it, click System and Security first.
-
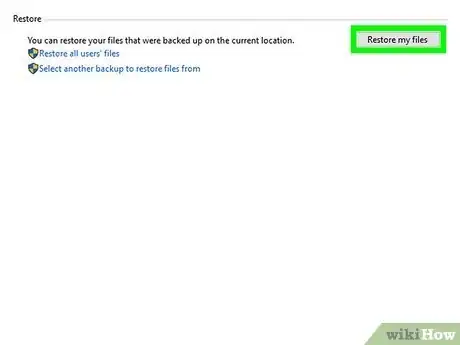
3Choose which files to restore. If you want to restore one of your own files, select Restore my files. To restore files for another user (or all users), choose Restore all users' files.
- If you want to restore files from a different backup than the one selected by default, click Select another backup to restore files from, and then locate the backup.
-
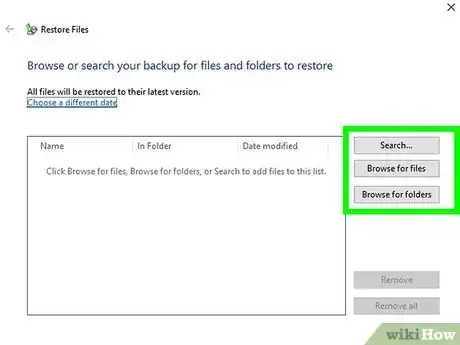
4Select Browse for files or Browse for folders. Choose the option that applies to you based on whether you want to restore individual files or entire folders.
-
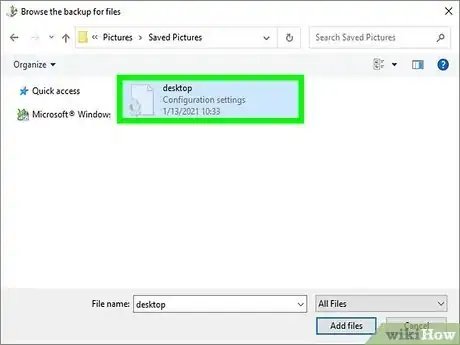
5Search for the file or folder you want to restore. You can type any part of the file or folder name to locate the file or folder, and then click Search.
- You can use wildcards, such as *.jpg, to find all files that match a certain string of text.
-
6Select the file(s) or folder(s) and click Next.
-
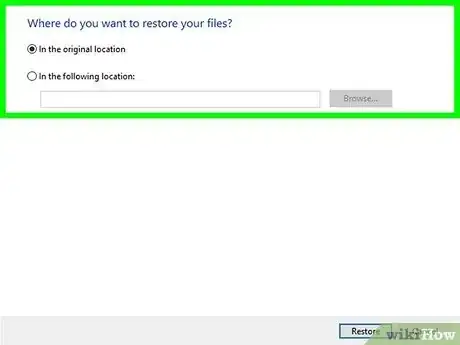
7Choose where you want to restore the files. To bring them back to their original location, leave the default option selected. Otherwise, you can select In the following location and click Browse to select another folder.
-
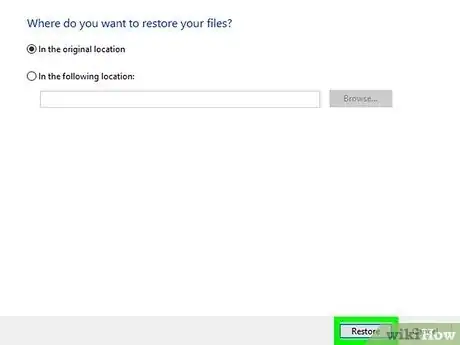
8Click Restore. The selected file(s) and/or folder(s) will be recovered to the chosen directory.
Using Stellar Data Recovery (Paid Option)
-
1Install Stellar Data Recovery on your Windows PC. This file recovery app does have a fee, but you can do a free scan before paying to see if the app is capable of restoring the files you need. Search the web for "Stellar Data Recovery" and install the free downloadable version.
-
2Open Stellar Data Recovery. You'll find it in your Windows menu after installing.
-
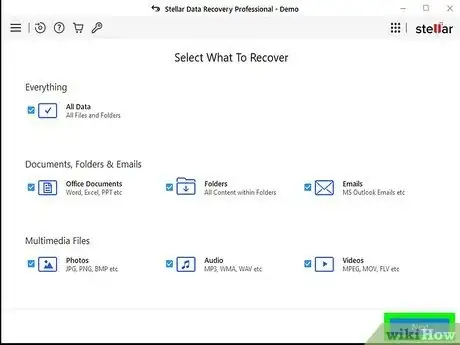
3Choose what you want to recover and click Next. You can select as many of the different file types as you'd like.
-
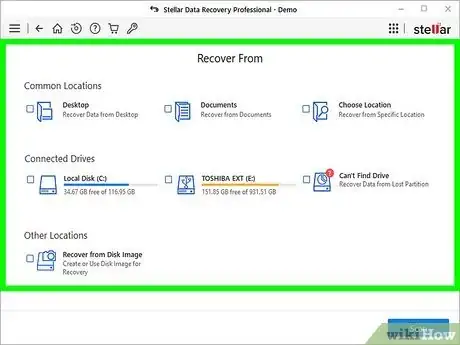
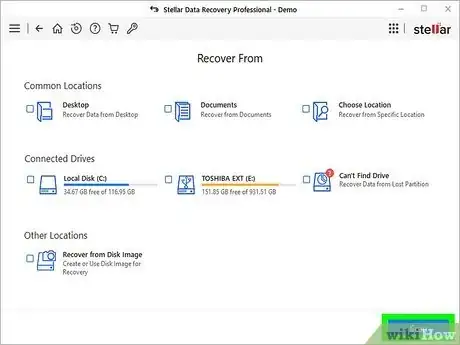
4Select the location from which you deleted the file. You can choose one of the common locations at the top, such as Desktop or Documents, or select Choose Location to select a folder manually.
- If the file was saved to an external drive that's connected to your computer right now, select that drive.
- If the file was saved to a partition that is no longer accessible, select Can't Find Drive.
-
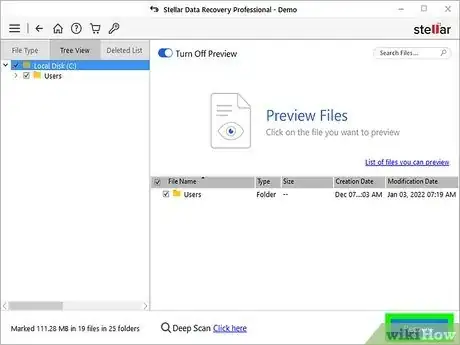
5Click Scan to search for deleted files. Once the scan is complete, you'll see a list of files and/or folders you can restore.
- If nothing is found, click the link next to "Deep Scan" to try a more in-depth scan.
-
6Select the file(s) and/or folder(s) and click Recover. If you're willing to pay for Stellar, you will be asked to do so now. Once you make your payment, you'll receive a product key via email that you can enter into the provided field. Once validated, you'll be able to recover the selected file(s), as well as any you need to recover in the future.
Expert Q&A
-
QuestionHow can I recover a file that was accidentally overwritten?
 Stan KatsStan Kats is the COO and Chief Technologist for The STG IT Consulting Group in West Hollywood, California. Stan provides comprehensive technology & cybersecurity solutions to businesses through managed IT services, and for individuals through his consumer service business, Stan's Tech Garage. Stan has over 7 years of cybersecurity experience, holding senior positions in information security at General Motors, AIG, and Aramark over his career. Stan received a BA in International Relations from The University of Southern California.
Stan KatsStan Kats is the COO and Chief Technologist for The STG IT Consulting Group in West Hollywood, California. Stan provides comprehensive technology & cybersecurity solutions to businesses through managed IT services, and for individuals through his consumer service business, Stan's Tech Garage. Stan has over 7 years of cybersecurity experience, holding senior positions in information security at General Motors, AIG, and Aramark over his career. Stan received a BA in International Relations from The University of Southern California.
Cybersecurity Expert If you hadn't turned on file versions in your operating system, and you overwrote a file with the exact same name, then unfortunately it will have been lost irrevocably. Check to see if you made backup copies.
If you hadn't turned on file versions in your operating system, and you overwrote a file with the exact same name, then unfortunately it will have been lost irrevocably. Check to see if you made backup copies.
References
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/recover-lost-files-on-windows-10-61f5b28a-f5b8-3cc2-0f8e-a63cb4e1d4c4
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/backup-and-restore-in-windows-352091d2-bb9d-3ea3-ed18-52ef2b88cbef
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/file-history-in-windows-5de0e203-ebae-05ab-db85-d5aa0a199255
- ↑ https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/tech-tips-and-tricks/recover-deleted-files.html
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/back-up-and-restore-your-pc-ac359b36-7015-4694-de9a-c5eac1ce9d9c
About This Article
1. Check the Recycle Bin first.
2. Use Windows File Recovery if you have another drive, including a flash drive.
3. Restore from File History if you make backups.
4. Use the free Recuva tool to find deleted files.
5. Restore from an older backup using Backup and Restore.
6. Try Stellar Data Recovery's free option to see if files are recoverable.







-Step-17.webp)








-Step-17.webp)