This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD. Jennifer Mueller is a wikiHow Content Creator. She specializes in reviewing, fact-checking, and evaluating wikiHow's content to ensure thoroughness and accuracy. Jennifer holds a JD from Indiana University Maurer School of Law in 2006.
This article has been viewed 44,188 times.
Learn more...
A protractor is a handy tool that allows you to precisely measure the number of degrees in any angle. The typical protractor is made of clear plastic and has two sets of numbers around the edge. The numbers you use depend on whether the angle you're measuring is acute (less than 90 degrees) or obtuse (more than 90 degrees but less than 180). If you're dealing with a reflex angle (more than 180 degrees but less than 360), you'll have to do an additional calculation.[1]
Steps
Measuring Acute and Obtuse Angles
-
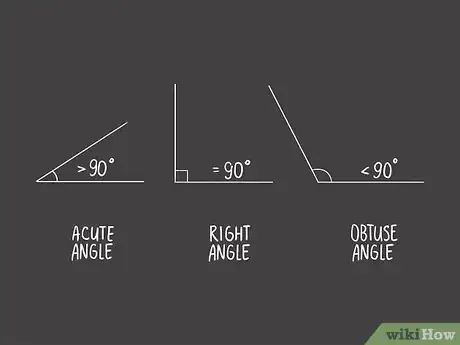
1Determine what type of angle you're measuring. A right angle is exactly 90 degrees. If an angle is less than 90 degrees, it's an acute angle. Obtuse angles, on the other hand, are more than 90 degrees but fewer than 180.[2]
- In some diagrams, you may see more than one angle. The arc around the vertex shows you which angle you're supposed to find the value of.
- Labeling an angle acute or obtuse helps you reading the protractor. For example, if you know you have an obtuse angle, then you know it is going to be more than 90 degrees. If you get a smaller number from your protractor, you're likely looking at the wrong scale.
-
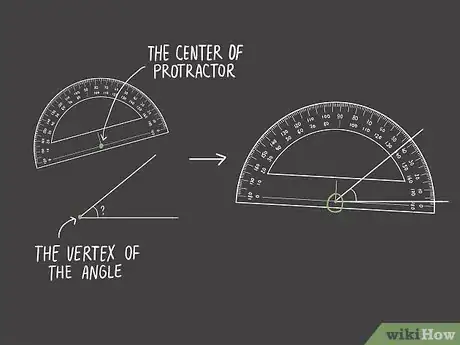
2Place the center of your protractor on the vertex of the angle. At the bottom of your protractor, you'll see a little hole in the center. Typically this hole has vertical and horizontal lines crossing it, so you can line up the protractor exactly.[3]
- To make sure you're right on the vertex, it can help to make a little dot inside the center of your protractor. Then remove your protractor and confirm the dot is on the exact tip of the vertex.
Advertisement -
3Line up one line with the protractor's baseline. The baseline of your protractor is the solid line on the bottom with a "0" at either end. Once you have the protractor on the vertex of the angle, adjust either the protractor itself or your paper until one line is following the baseline.[4]
- If one line is more horizontal, it will typically be the easiest one to line up along the baseline. However, you'll get the same result no matter which line you use.[5]
-
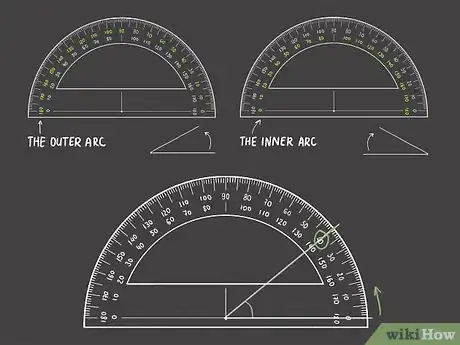
4Find the degrees in the angle using the correct scale. Along the outside of the protractor are 2 arcs of numbers. Use the outer arc if the angle you're measuring opens to the left. Use the inner arc if the angle you're measuring opens to the right. The number that the other line of the angle crosses is the number of degrees in that angle.[6]
- Protractors usually provide numbers in 10s. If the angle you're measuring doesn't line up perfectly with a number, count the hash marks on the outside edge of the protractor to determine the degrees in that angle.
Tip: To visualize whether the angle opens to the right or the left, imagine the angle rays are an alligator's jaws. No matter how wide, the direction the alligator is pointing when its "jaws" are closed is the direction the angle opens.
Calculating Reflex Angles
-
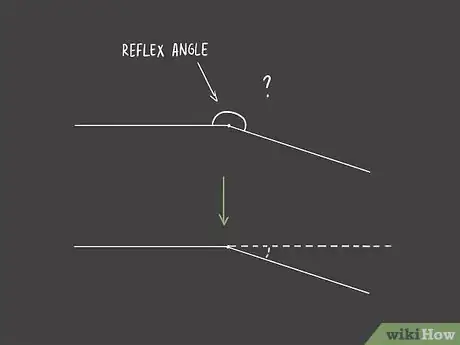
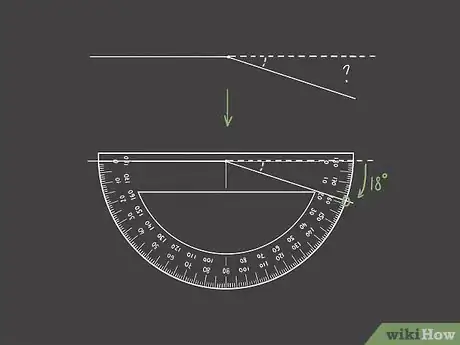
1Draw a straight line from the vertex of the angle. Line up the straight edge of your protractor under the horizontal line of the angle. Extend the line straight out from the vertex across the other side.[7]
- If you look below the straight line, you'll see another angle. This smaller acute angle is formed by the straight line you drew and the diagonal line of the original reflex angle.
-
2Place your protractor on the straight line to measure the acute angle. Line up the horizontal line on the baseline of your protractor, placing the center of your protractor over the vertex. Look where the diagonal line crosses the protractor to determine the number of degrees in the acute angle.[8]
- You may find it easier to measure if you turn your paper so that the acute angle is facing straight up.
-
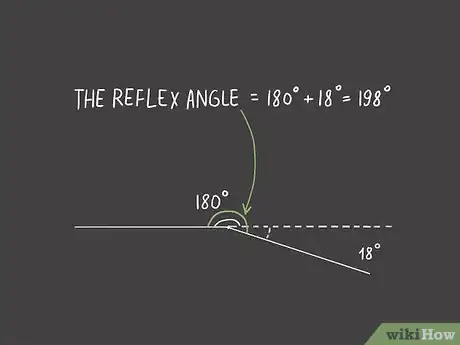
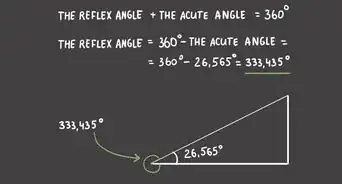
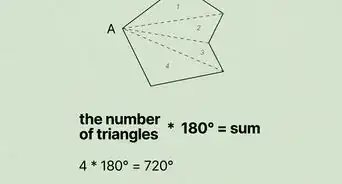
3Add the measurement of the acute angle and 180. A reflex angle is more than 180 degrees, but less than 360. The acute angle you just measured plus 180 degrees will give you the degrees in the reflex angle.[9]
- For example, if the reflex angle produces an acute angle of 18 degrees, that would mean the reflex angle is 198 degrees.
Variation: There are full-circle protractors that eliminate the need for this additional math.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow do I know which arc to use when measuring any angles?
 DonaganTop AnswererThe arcs are identical in terms of angular measurement. One arc begins with 0° on the right side. The other arc begins with 0° on the left side. Use the arc that allows you to measure an angle in the direction you prefer: clockwise or counter/anticlockwise.
DonaganTop AnswererThe arcs are identical in terms of angular measurement. One arc begins with 0° on the right side. The other arc begins with 0° on the left side. Use the arc that allows you to measure an angle in the direction you prefer: clockwise or counter/anticlockwise.
References
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/reflex.html
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/articles/zpjh97h
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/zrck7ty/revision/4
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/zrck7ty/revision/4
- ↑ https://www.onlinemathlearning.com/measuring-angles.html
- ↑ https://www.onlinemathlearning.com/measuring-angles.html
- ↑ https://www.mathsteacher.com.au/year7/ch08_angles/01_ang/ang.htm
- ↑ https://www.mathsteacher.com.au/year7/ch08_angles/01_ang/ang.htm
- ↑ https://www.mathsteacher.com.au/year7/ch08_angles/01_ang/ang.htm
About This Article
To measure an angle using a protractor, place the center of your protractor at the vertex of the angle, which is where the two lines come to a point. Then, line up one line with the protractor’s baseline, which is the solid line on the bottom with a “0” at either end. Once your protractor is positioned correctly, see what number the other line of the angle crosses. If your angle opens to the left, you should note the number on the outer arc of the protractor. Otherwise, if your angle opens to the right, use the number in the inner arc. Sometimes the line of the angle may not line up perfectly with a number, and if that’s the case, just count the hash marks on the outside edge to figure out the degrees. For more help, including how to calculate reflex angles with a protractor, read on!