This article was co-authored by Lauren Kurtz and by wikiHow staff writer, Amber Crain. Lauren Kurtz is a Naturalist and Horticultural Specialist. Lauren has worked for Aurora, Colorado managing the Water-Wise Garden at Aurora Municipal Center for the Water Conservation Department. She earned a BA in Environmental and Sustainability Studies from Western Michigan University in 2014.
There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 187,806 times.
When you cultivate a garden, you want to make sure your plants grow in the healthiest conditions possible. There’s no nutrient more important to the health of your garden than nitrogen! However, not all soil contains the best amount of nitrogen for plants to grow to their fullest potential. Use the right types of plant or animal waste to provide your soil with more nitrogen, so your garden can flourish the way you want![1]
Steps
Boosting Nitrogen with Fertilizer
-
1Use chemical fertilizer when you need a quick solution. Synthetic fertilizer is fast-acting and easy to apply. If you're in the middle of a growth season and your plants are suffering from nutritional deficiency, consider using chemical fertilizer to revive them. You can buy a wide range of chemical fertilizers at any home improvement center or nursery.[2]
- Keep in mind that chemical fertilizers are not a long-term solution. Over time, synthetic fertilizers diminish soil fertility.
-
2Buy fertilizer products tailored to your specific plants. When it comes to chemical fertilizers, the formulas make a big difference. If you're trying to boost nitrogen in your vegetable garden, buy fertilizer made specifically for vegetables. If your lawn needs a nitrogen boost, get a fertilizer formulated for grass. Specific formulas will release nutrients in a targeted way that is ideal for that plant type.[3]Advertisement
-
3Read the N-P-K numbers on fertilizer labels. All fertilizers are categorized by a 3 number rating system. The first number is nitrogen (N), the second number is phosphorous (P), and the third is potassium (K). These numbers represent the percentage of each nutrient found in the fertilizer. Always check the N-P-K before purchasing a product.[4]
-
4Choose a nitrogen level that matches your soil's needs. For example, 27-7-14 and 21-3-3 are popular nitrogen-heavy fertilizers that will also deliver a small amount of phosphorous and potassium to the soil. A 21-0-0 fertilizer will deliver only nitrogen to your soil. You can use a balanced blend like 10-10-10 or 15-15-15 if your soil needs all 3 nutrients replenished.[5]
-
5Go with a quality, slow release fertilizer. Slow release or controlled release fertilizers may cost a little more, but in the long run they are the best choice. With slow release formulas, you will be fertilizing your soil less frequently because they are longer lasting. They're also more effective because they release nutrients slowly and steadily.[6]
- Cheaper products can sometimes shock and burn plants, causing a horde of new problems.
- Since chemical fertilizers can negatively affect the soil over time, less frequent applications can help preserve the health of your soil.
- Slow release fertilizers often come in the form of pellets.
Using Plant Waste
-
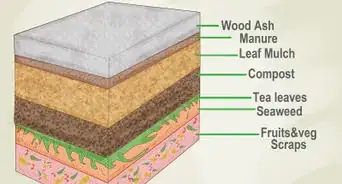
1Create compost out of vegetables, coffee grounds, and other food waste. Collecting food waste from your kitchen is the easiest way to enrich your soil with lots of nitrogen. It will take several months for your compost to “ripen” enough for use. Start the composting process in early summer so it will be ready by the following spring planting season.[7]
- Some other ingredients to use include tea bags, old condiments, rotting bread, corn cobs, leftover nut shells, fruit rinds, and much more.
- In the case of shells (from shellfish, nuts, or eggs) and fruit pits, it’s best to smash them up with a hammer or another heavy tool before putting them in compost.[8]
- Avoid adding bones, cheese, meat, oils, or animal waste to your compost.
-
2Add leftover grass clippings and garden trimmings to your compost. The garden waste you create while manicuring your yard can still be put to good use! Before you sprinkle garden waste into your batch of compost, shred it up into small pieces by hand. Mix the garden waste into the rest of the compost to distribute it evenly.[9]
- Spread the grass clippings across a towel for a few hours to let them dry before dumping them into your compost. Otherwise, the grass may rot in a wet mass and leave behind an unpleasant odor.[10]
-
3Spread alfalfa meal on top of your soil. Alfalfa meal is very strong; it heats up as it decays, and acts quickly. Because of this, you don’t want to add it deep into the soil or it could overload it. Alfalfa meal will provide the soil with plenty of nitrogen, as well as potassium and phosphorus.[11]
-
4Plant legume seeds, like peas, alfalfa, and beans. Legume plants are naturally much higher in nitrogen than other types of garden vegetables. As your legume plants grow, they will contribute extra nitrogen to the soil, making the soil richer and giving your other plants the nutrients they need.[12]
Distributing Animal Waste
-
1Mix feather meal with fertilizer and spread it during autumn. Feather meal is dried and ground chicken feathers. If you don’t keep your own chickens, you can obtain feather meal from a local garden center. Measure out around 1⁄3 cup (79 ml) of feather meal for each plant or 12 pounds (190 oz) for every 1,000 square feet (93 m2) of your garden. Mix it into your fertilizer of choice before spreading it over the soil.[13]
-
2Work crab meal into your soil before planting your spring crops. Crab meal is made from blue crab organs and shells, and can be obtained from a garden center. Distribute the crab meal (with fertilizer) across damp soil before running a tiller across the area. The crab meal will not only nourish your soil with plenty of nitrogen, but also protect your plants from being eaten by nematodes.[14]
- Turn your tiller to its medium depth setting (if your soil is moist) or its most shallow depth setting (if your soil is hard). Move the tiller in straight lines all throughout your gardening area.[15]
- Let the crab meal rest within the soil for anywhere from 3 days to 3 weeks. The nutrients will begin to break down and seep into the soil.[16]
-
3Soak fish emulsion into your soil. Fish emulsion is ground up fish parts. Look for it at your local garden center. Add the fish emulsion to your soil on a monthly basis; make sure to distribute enough for it to soak into the soil. Alternatively, add it to a large amount of water and sprinkle it over your plants.
- You may want to cover your mouth and nose as you use fish emulsion; it has a very strong, unpleasant smell![17]
- Keep pets away from your fresh fertilizer if you use fish emulsion so they don't dig up your plants.
-
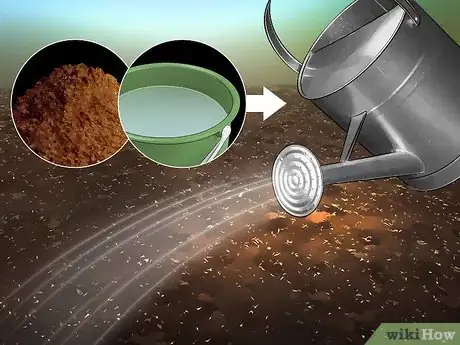
4Water your garden with blood meal. Blood meal is dried animal blood. You can obtain it from your local garden center. While the idea of using blood meal to nourish your soil may sound gruesome, blood meal is actually rich with nitrogen. Blend the blood meal with water prior to using it, then distribute it with a simple watering can.[18]
- Alternatively, you can sprinkle it in a hole in the soil before you plant your next crop.
Fertilizing with Animal Manure
-
1Pick manure produced from poultry or livestock. Sheep, chickens, rabbits, cows, pigs, horses, and ducks are all excellent sources of nitrogen-rich manure. The manure of these animals will nourish your soil with nitrogen and many other nutrients, including zinc and phosphorus.
- You can also buy aged manure from your local garden center.
-
2Use only 6 month old (or older) manure. It isn’t necessarily the disease potential that makes extremely fresh manure unsafe to use (though that’s a contributing factor). New manure contains far too much nitrogen for your dirt to absorb. Too much nitrogen can keep seeds from sprouting after planting, as the excess nitrogen will burn them up at the roots.[19]
-
3Put on gloves prior to handling animal manure. Manure can easily spread disease. Protect yourself from any negative effects by wearing the right gear. After distributing the manure, scrub your hands and nails under warm water with antibacterial soap.[20]
-
4Add manure-based compost a minimum of 60 days before you plant. Wait a minimum of 60 days so that your soil can absorb the nutrients in the manure. This will also reduce any potential health effects from eating produce that made contact with the manure. Either add it in dried form to a compost, or spread fresher manure directly over your soil. If you decide to turn the manure into compost, be sure to mix it well with the rest of your ingredients.
- To really revitalize your soil and prepare it for the next planting season, distribute manure-based compost across your garden during the autumn months. The nutrients will soak into the soil over winter.
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionHow can I increase the nitrogen availability in my soil?
 Lauren KurtzLauren Kurtz is a Naturalist and Horticultural Specialist. Lauren has worked for Aurora, Colorado managing the Water-Wise Garden at Aurora Municipal Center for the Water Conservation Department. She earned a BA in Environmental and Sustainability Studies from Western Michigan University in 2014.
Lauren KurtzLauren Kurtz is a Naturalist and Horticultural Specialist. Lauren has worked for Aurora, Colorado managing the Water-Wise Garden at Aurora Municipal Center for the Water Conservation Department. She earned a BA in Environmental and Sustainability Studies from Western Michigan University in 2014.
Professional Gardener
-
QuestionIf I'm making a compost-based fertilizer with shells and food waste, how long before I can start using it?
 Lauren KurtzLauren Kurtz is a Naturalist and Horticultural Specialist. Lauren has worked for Aurora, Colorado managing the Water-Wise Garden at Aurora Municipal Center for the Water Conservation Department. She earned a BA in Environmental and Sustainability Studies from Western Michigan University in 2014.
Lauren KurtzLauren Kurtz is a Naturalist and Horticultural Specialist. Lauren has worked for Aurora, Colorado managing the Water-Wise Garden at Aurora Municipal Center for the Water Conservation Department. She earned a BA in Environmental and Sustainability Studies from Western Michigan University in 2014.
Professional Gardener The process of composting shells and food waste into usable compost takes anywhere from 3 to 6 months. Once you have a large pile of compost scraps, the pile must rest for several months to decompose. During this time the pile will need to be watered and mixed every few weeks. After you mix the compost into your soil, you can plant immediately or wait a few days.
The process of composting shells and food waste into usable compost takes anywhere from 3 to 6 months. Once you have a large pile of compost scraps, the pile must rest for several months to decompose. During this time the pile will need to be watered and mixed every few weeks. After you mix the compost into your soil, you can plant immediately or wait a few days. -
QuestionHow can I measure nitrogen in soil?
 Community AnswerTo check for the presence of nitrogen, you could use a pH indicator/Universal Indicator. You would probably need to send a sample to a lab for a precise measurement.
Community AnswerTo check for the presence of nitrogen, you could use a pH indicator/Universal Indicator. You would probably need to send a sample to a lab for a precise measurement.
References
- ↑ http://ccetompkins.org/resources/getting-the-most-out-of-your-vegetable-garden-soil-test-report
- ↑ http://www.garden-counselor-lawn-care.com/chemical-fertilizer.html
- ↑ http://www.garden-counselor-lawn-care.com/chemical-fertilizer.html
- ↑ http://www.garden-counselor-lawn-care.com/fertilizer-numbers.html
- ↑ http://www.garden-counselor-lawn-care.com/fertilizer-numbers.html
- ↑ http://www.garden-counselor-lawn-care.com/chemical-fertilizer.html
- ↑ http://www.bhg.com/gardening/yard/compost/how-to-compost/
- ↑ http://www.compostjunkie.com/compost-ingredients.html
- ↑ https://www.the-compost-gardener.com/composting-grass.html
- ↑ https://www.the-compost-gardener.com/composting-grass.html
- ↑ https://www.rodalesorganiclife.com/garden/grow-healthier-crops-using-these-natural-nitrogen-sources
- ↑ https://www.rodalesorganiclife.com/garden/grow-healthier-crops-using-these-natural-nitrogen-sources
- ↑ http://www.bettervegetablegardening.com/feather-meal-fertilizer.html
- ↑ https://www.rodalesorganiclife.com/garden/grow-healthier-crops-using-these-natural-nitrogen-sources
- ↑ https://youtu.be/z9_s1zm-muY?t=1m24s
- ↑ https://youtu.be/z9_s1zm-muY?t=2m1s
- ↑ https://www.rodalesorganiclife.com/garden/grow-healthier-crops-using-these-natural-nitrogen-sources
- ↑ https://www.rodalesorganiclife.com/garden/grow-healthier-crops-using-these-natural-nitrogen-sources
- ↑ https://piedmontmastergardeners.org/article/manure/
- ↑ http://anrcatalog.ucanr.edu/pdf/8366.pdf
About This Article
To increase nitrogen in soil, try making compost using vegetables, coffee grounds, and other food waste, which will enrich your soil with nitrogen when you use it to garden with. You can also plant more legume plants, like peas, alfalfa, and beans, which produce nitrogen as they grow. If you're looking for a quick fix, try mixing a chemical fertilizer into the soil to increase the nitrogen levels. Or, go with a slow-release fertilizer, which will last longer and be more effective. For more tips from our Horticulture co-author, like how to increase nitrogen in soil using animal waste, scroll down!