This article was co-authored by Ben Barkan and by wikiHow staff writer, Hannah Madden. Ben Barkan is a Garden and Landscape Designer and the Owner and Founder of HomeHarvest LLC, an edible landscapes and construction business based in Boston, Massachusetts. Ben has over 12 years of experience working with organic gardening and specializes in designing and building beautiful landscapes with custom construction and creative plant integration. He is a Certified Permaculture Designer, is licensed Construction Supervisor in Massachusetts, and is a Licensed Home Improvement Contractor. He holds an associates degree in Sustainable Agriculture from the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 9,875 times.
Are your plants looking a little lackluster, or not growing as quickly as they should be? If so, your soil could be lacking phosphorus. This important nutrient is essential to any crop you’ll grow, and fortunately, there are ways you can add it to your soil using natural and organic products. In this article, we’ll tell you exactly how to add phosphorus to your soil, as well as when to add it and how to know if your soil needs it.
Things You Should Know
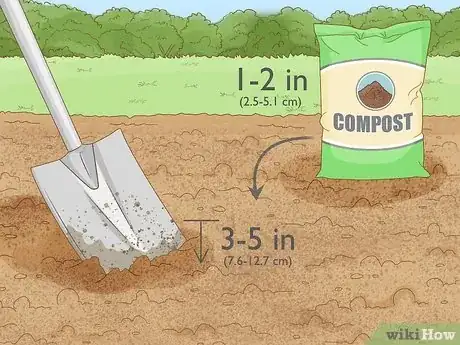
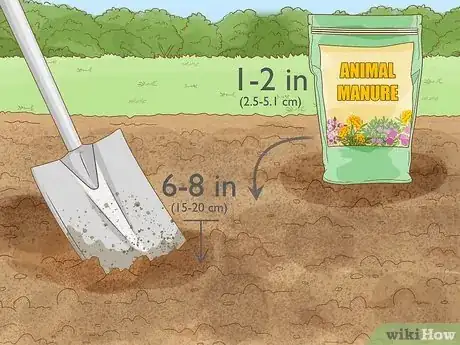
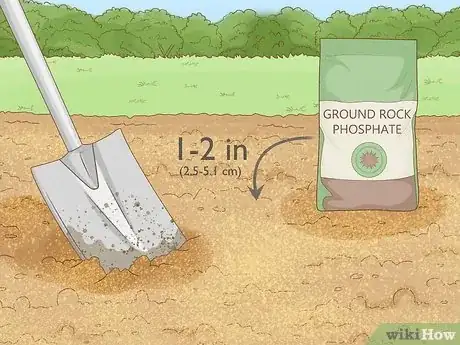
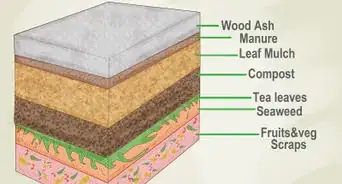
- Use compost, animal manure, bone meal, rock phosphate, or green manure for natural sources of phosphorus.
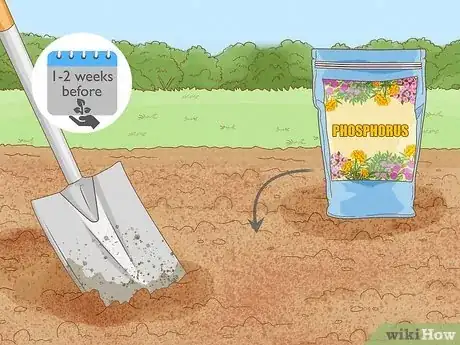
- Add it to your soil 1-2 weeks before you plant for best results. You can also add it during the growing season to give your plants a little extra oomph.
- Check for stunted plant growth or a dark green coloring on your plants to determine if you need to add phosphorus. You can also use a soil test kit.
Steps
When to Add Phosphorus to Soil
-
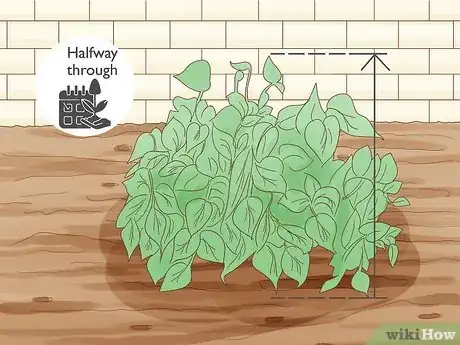
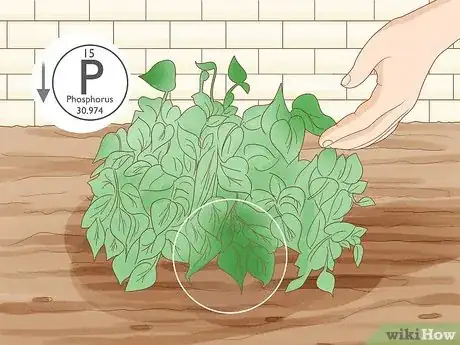
1Add phosphorus to your soil 1 to 2 weeks before planting for best results. Phosphorus usually takes a couple of weeks to be released into the soil. You can use phosphorus at any point in the season, but give your soil a few weeks to absorb it before you start planting.[7]
-
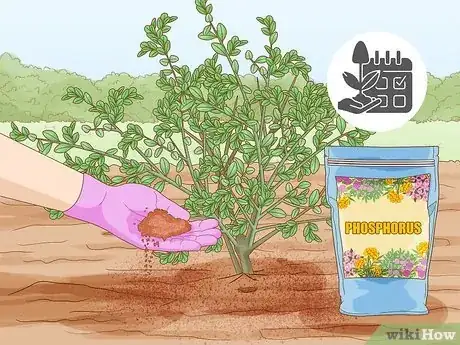
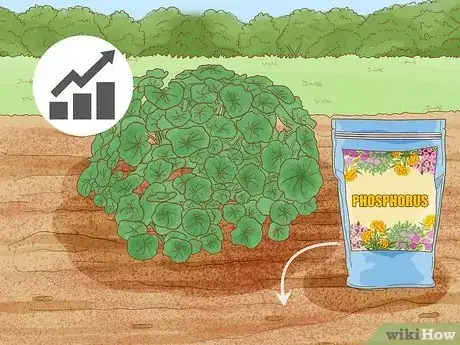
2Mix phosphorus into the soil during the growing season to give your plants a boost. If you’ve already planted your crops and you’ve noticed them looking a little blah, you can absolutely add phosphorus to the soil around your plants. Simply sprinkle your phosphorous product, like compost, around the plants, and carefully mix it with the top layer of dirt without disturbing the roots of your crops.[8]
References
- ↑ https://ag.umass.edu/vegetable/fact-sheets/compost-use-soil-fertility
- ↑ https://earthmatter.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/tip-sheet-how-to-use-compost-cpts-htuc-f.pdf
- ↑ https://extension.unh.edu/resource/guidelines-using-animal-manures-and-manure-based-composts-garden-fact-sheet
- ↑ https://s3.wp.wsu.edu/uploads/sites/403/2015/03/bonemeal.pdf
- ↑ https://extension.umn.edu/phosphorus-and-potassium/understanding-phosphorus-fertilizers
- ↑ https://cdn.dal.ca/content/dam/dalhousie/pdf/faculty/agriculture/oacc/en/technical-bulletins/2006/OACC_Technical_Bulletin_2006_17_web.pdf
- ↑ https://www.globalnetacademy.edu.au/grow-better-root-vegetables-by-adding-phosphorus-to-your-soil/
- ↑ https://www.hortmag.com/smart-gardening/compost-improves-the-garden
- ↑ https://passel2.unl.edu/view/lesson/0718261a1c9d/2