X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 30,094 times.
Learn more...
Scalable Vector Graphics are a very powerful and convenient file type for computer graphics. Unlike other rasterized file types, SVGs can be scaled without any quality loss. This makes them perfect for certain graphics such as logos. In order to use SVGs on your website, you need to embed them in your HTML.
Steps
-
1Create a graphic using a vector based graphics software
- Any vector based graphic software will do, as long as it has the ability to save documents as an SVG
- It will be useful to design your graphic at the size that you intend for it to appear on the page, however, you will be able to dynamically change the size using CSS later on.
-
2Organize the groups and layers of your graphic.
- Within your graphic editor, it is very useful to keep your image well organized. Doing so will make future steps far easier.
- In Adobe Illustrator, group paths together by holding shift and selecting multiple paths. Then, right click and choose "group." You will see your new groups in the layers window.
Advertisement -
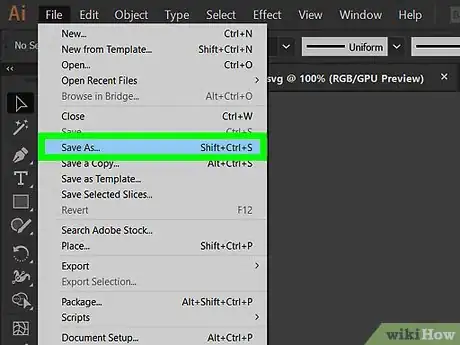
3Save your graphic as an SVG.
- Any vector based graphics editor will should allow you to save your graphic as an SVG.
- In illustrator, select "Save As" from the file tab. In the dialog box, select SVG from the dropdown list, then click save.
- You may encounter an "SVG Options" dialog box. There are several versions of the SVG file format, generally, version 1.1 is fine. Select OK and continue.
-
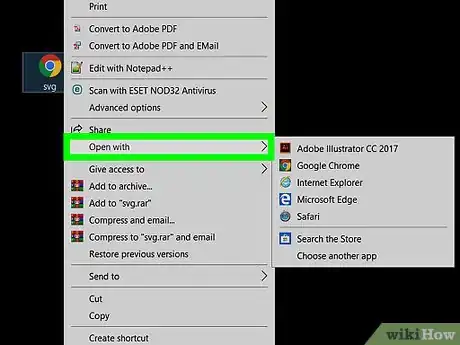
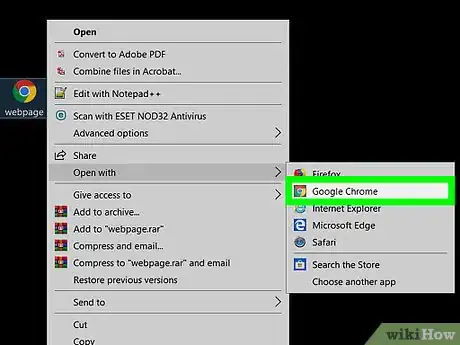
4Open your SVG in a text editing software.
- In the file explorer, right click your new SVG file and select "Open with" from the list.
- From the available programs, select any text editor. You may need to select "More Apps" or "Choose another app" if your desired text editor is not in the list.
- Notepad is fine, however, you may choose to open your SVG in an IDE such as Visual Studio.
-
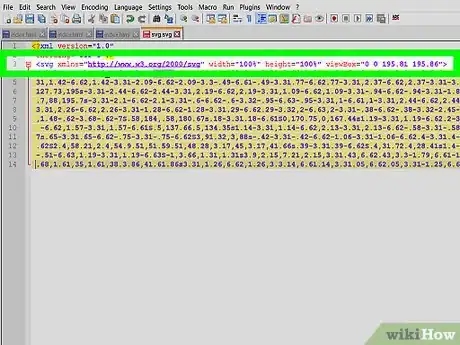
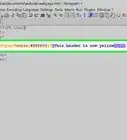
5Copy the SVG tag.
- Once opened, use your cursor to select only the contents of the <svg> tag.
- There will be a line at the top of the file that begins with "<?xml ..." Ignore this line and any additional comment lines at the top of the document.
- Everything within the <svg> tags is valid HTML markup and may be placed in an HTML page.
-
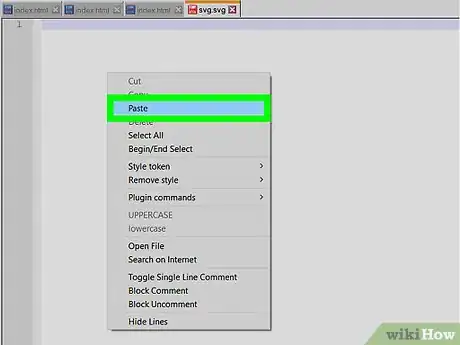
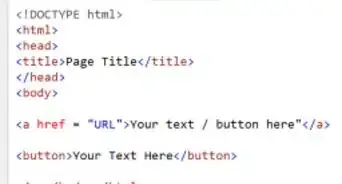
6Paste the SVG into your HTML page.
- Open your HTML page in a text editor and paste the block of code you copied from the last step into your web page.
- The SVG tag may be place anywhere in the body of your HTML markup.
-
7Check your results in a web browser
- Open your web page in a browser and your graphic will appear on your page, however, it may require some extra styling to properly format the graphic within your page.
- If your graphic is already sized properly and appears as you desire it, you may stop after this step.
-
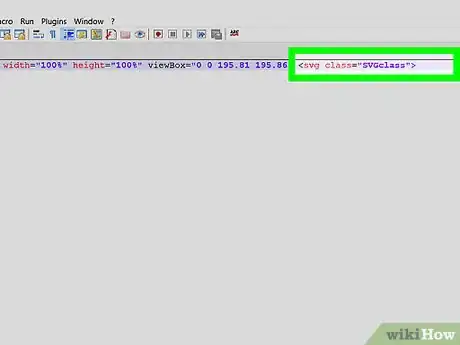
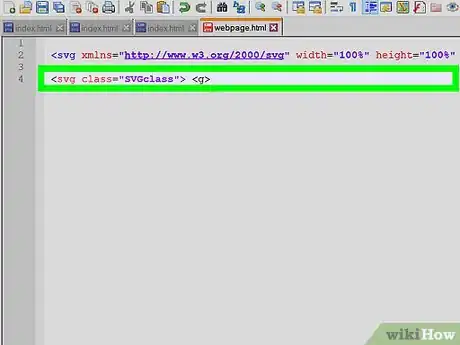
8Give your SVG a class attribute
- It will be useful to give your SVG a descriptive class for styling
- In some instances a class attribute may already exist on the SVG tag. If this is the case, simply add classes to the existing attribute.
- e.g <svg class="SVGclass" ...
-
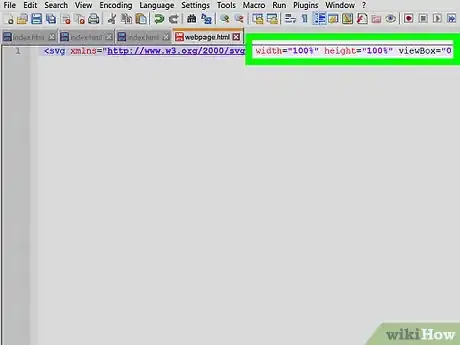
9Adjust the size of your graphic if it is not already the proper size
- If your graphic appears to large or too small on your page, you can adjust its size using CSS or HTML attributes.
- One of the benifits of the SVG format is that it may be scaled to any size without quality loss.
- Within the angle brackets of the SVG, you may create two new attributes for width and height if they do not already exist. e.g width="150" height="200". The value within the quotation marks indicates the pixel dimensions of the graphic
- Alternativley, you may set the dimensions using CSS by targeting the class that you assigned to your SVG. e.g .SVGclass{ width: 200px }
-
10Organize the markup of your SVG. This step will make any further styling using CSS much easier.
- Each <g> tag within the markup of the SVG represents a group that you created in your graphics software.
- Comment, or add custom classes to the tags withing your SVG so that they may be targeted with CSS
-
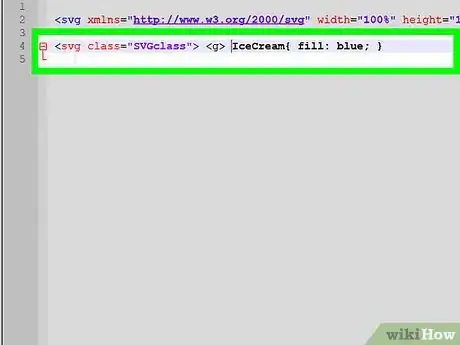
11Use CSS to modify your SVG
- SVGs are comprised of different tags that behave like other HTML elements. They can be given style and class attributes for styling.
- Paths and shapes within your svg can have their fill, stroke, stroke-width, and many other styles edited with CSS.
- For example: .IceCream{ fill: blue; }
-
12View the results in a web browser.
- All of your new styling should be visible within a web browser.
- Repeat steps 10 and 11 until you graphic has all of the desired styling.
Advertisement
Things You'll Need
- Any vector based graphic editing software such as Adobe Illustrator
- Any text editing software or IDE
- Any web browser
- An HTML page that you intend to embed your graphic into
About This Article
Advertisement