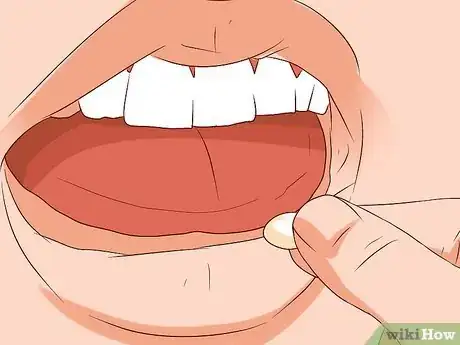This article was co-authored by Chris M. Matsko, MD. Dr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 250,462 times.
Sublingual medications are orally disintegrating or dissolving medications that are administered by being placed under the tongue. These medications are transferred to the bloodstream from the mucous membranes in the mouth after dissolving, allowing for quick absorption that avoids the loss of potency which may come with first-pass metabolism in the stomach and liver.[1] Doctors may recommend sublingual medications to treat certain conditions, or if a patient has trouble swallowing or digesting medication.[2] Understanding how to administer sublingual medication can help ensure proper dosing and efficacy of the medication.
Steps
Preparing to Administer Sublingual Medication
-
1Wash your hands. This should be done before and after administering medication in order to prevent the spread of germs and infectious diseases.
- Lather anti-bacterial hand soap between hands, working between fingers and under fingernails. Scrub for at least 20 seconds.[3]
- Rinse hands thoroughly under warm water. Be sure that all soap is washed off, and any visible dirt is gone.
- Dry hands with a clean, disposable paper towel.
-
2Put on clean, disposable gloves if administering medication to someone else. Wearing latex or nitrile gloves prevents germs from being passed to the patient, and also protects the person administering medication.
- Be sure that your patient does not have a latex allergy before using latex gloves.
Advertisement -
3Double-check that the medication is prescribed to be taken sublingually. Taking non-sublingual medications under the tongue can reduce the efficacy of that medication. Common sublingual medications include:
- heart medication (such as nitroglycerin and verapamil)
- certain steroids
- certain opioids
- certain barbiturates
- enzymes
- certain vitamins and minerals
- certain mental health medications[4]
-
4Double-check the frequency and dosage of medication prescribed. Before taking or administering any medication, it is important to confirm that the correct dosage is prepared and is being taken/given at the proper intervals.
-
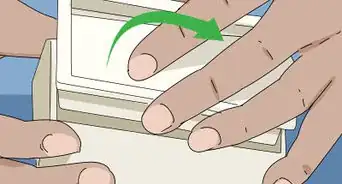
5Cut the pill, if necessary. Some oral medications only require that a portion of the pill be taken, if it is being administered sublingually. If this is the case, you may need to cut the pill before it can be taken.
- Use a pill cutter if at all possible. This is more precise than simply breaking a pill apart by hand or using a knife.
- Clean the blade before and after cutting the pill. This is important, both to prevent the pill from being contaminated and from accidentally contaminating other medications.
Administering Sublingual Medication
-
1Sit upright. The person taking any medication should always be situated in an upright sitting position before medication is administered.
- Do not allow the individual to lie down or try to administer the medication when the person is unconscious. This could lead to accidental aspiration of the medication.
-
2Do not eat or drink when administering medication. Rinse your mouth out with water prior to administering medication. It's important not to eat or drink when sublingual medication is administered because this increases the risk of the medication being swallowed, which will make it less effective.[5]
-
3Do not smoke for at least an hour before you take sublingual medication. Cigarette smoke constricts the blood vessels and mucous membranes in the mouth, which will reduce the absorption level of the sublingual medication.[6]
-
4Be aware of the possible risks. Because sublingual medication is administered in the mouth, patients with open mouth sores may experience pain or irritation.[7] Eating, drinking, and smoking can all interfere with absorption and dosage rates. It is generally recommended that sublingual medications should not be used for prolonged periods of time.[8]
-
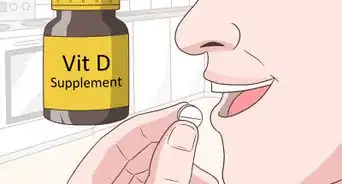
5Place the medication under the tongue. Medication can be administered on either side of the frenulum (the connective tissue under the tongue).
- Tilt head forward to avoid swallowing medication.
-
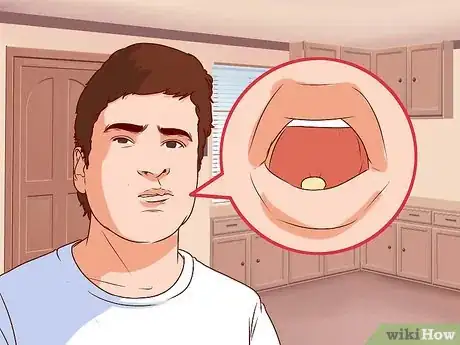
6Hold the sublingual medication under the tongue for the prescribed length of time. Most medications should have a dissolve time of approximately one to three minutes.[9] Avoid opening the mouth, eating, talking, moving or standing during this time to ensure that the tablet doesn't move and has time to dissolve completely and be absorbed.
- The onset of action of sublingual nitroglycerin is within 5 minutes and the duration can last up to 30 minutes. The amount of time it takes to dissolve may vary from one medication to the next. Consult with a pharmacist or talk to your doctor about how long it will take for your medication to dissolve sublingually.
- If the sublingual nitroglycerin is potent a subtle tingling sensation should be felt on the tongue.
-
7Do not swallow the medication. Sublingual medication needs to be absorbed under the tongue.
- Swallowing sublingual medication may cause erratic or incomplete absorption and could lead to improper dosing.[10]
- Ask your doctor or a pharmacist how to correct your dosage in case of accidental swallowing of sublingual medication.
-
8Wait before drinking or rinsing the mouth. This will ensure that the medication has dissolved completely and has had a chance to absorb into the mucous membranes.
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionHow soon can you drink hot coffee or tea after taking sublingual medication?
 Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Family Medicine Physician
-
QuestionWhat if a person is asleep? Can a sublingual medication like an antihypertensive be still given?
 Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Family Medicine Physician
Warnings
- Do not attempt to take any medication sublingually that was not prescribed as such. Some medications require digestive action to absorb, and may be less effective or even harmful if taken sublingually.[11]⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19062634
- ↑ http://www.hospicepatients.org/hospic67.html
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/features/handwashing/
- ↑ http://www.healthline.com/health/sublingual-and-buccal-medication-administration#Purpose2
- ↑ http://www.ijppsjournal.com/Vol3Suppl2/1092.pdf
- ↑ http://www.ijppsjournal.com/Vol3Suppl2/1092.pdf
- ↑ http://www.healthline.com/health/sublingual-and-buccal-medication-administration#Risks3
- ↑ http://www.healthline.com/health/sublingual-and-buccal-medication-administration#Risks3
- ↑ https://drmorgancamp.wordpress.com/2013/11/13/taking-your-supplements-and-medications-correctly/
About This Article
Before you administer sublingual medication, wash your hands with warm water and soap, and put on clean disposable gloves to prevent spreading germs. Then, double-check the instructions on the medication to make sure you’re administering the right frequency and dosage. When you’re ready to administer the medication, sit the patient upright, and place the pill under their tongue. Once the medication is in their mouth, have them hold it there until it dissolves, which should take 1-3 minutes. Make sure the patient doesn’t swallow the pill, as this can make it less effective. To learn how to use a pill-cutter to dose the medication properly, read more from our Physician co-author.