This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD. Jennifer Mueller is a wikiHow Content Creator. She specializes in reviewing, fact-checking, and evaluating wikiHow's content to ensure thoroughness and accuracy. Jennifer holds a JD from Indiana University Maurer School of Law in 2006.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 105,748 times.
Learn more...
Your synopsis describes the plan for your research project and is typically submitted to professors or department heads so they can approve your project. You might also submit a synopsis to organizations to get funding for a research project. Most synopses are between 3,000 and 4,000 words, although some are shorter. While the specific types of information you need to include in your synopsis may vary depending on your department guidelines, most synopses include the same basic sections.
Steps
Research Synopsis Template
Organizing Your Document
-
1Get formatting guidelines from your instructor or advisor. Specific formatting guidelines vary among disciplines and even among different programs in the same department. Your instructor or advisor will give you guidelines to follow.[1]
- Find out what citation format you're supposed to use as well, and whether you're expected to use parenthetical references or footnotes in the body of your synopsis.
-
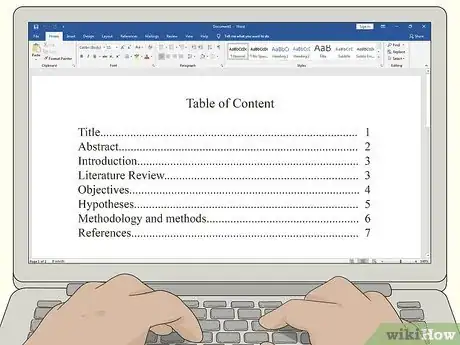
2Set up the headings for your sections. A synopsis typically uses standard headings for the different sections. Your department might have specific guidelines for how to format your headings so they stand out from the rest of the text. A typical synopsis has at least the following sections:[2]
- Title
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Objectives
- Hypotheses
- Methodology and methods
- References
Tip: Your synopsis might have additional sections, depending on your discipline and the type of research you're conducting. Talk to your instructor or advisor about which sections are required for your department.
Advertisement -
3Format your references. Generally, it's more efficient to format your list of references before you write your synopsis. That way, you don't have to stop writing to format a reference — you can just plug it in.[3]
- Keep in mind that you might not end up using all the sources you initially found. After you've finished your synopsis, go back and delete the ones you didn't use.
Drafting Your Synopsis Sections
-
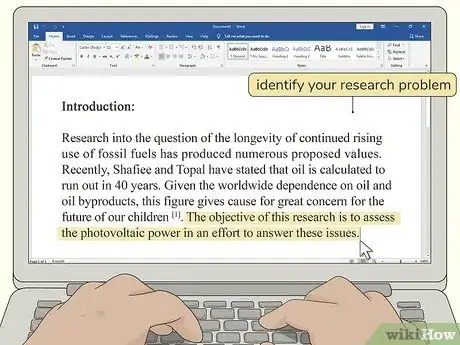
1Use the introduction to identify your research problem. Describe the problem or question that your research will address and discuss its importance to your field. Start by giving some background to put the problem into context and explaining how you want to approach it.[4]
- The introduction gives you the opportunity to set out for your reader exactly why the question you're trying to answer is vital and how your knowledge and experience make you the best researcher to tackle it.
- Support most of the statements in your introduction with other studies in the area that support the importance of your question. For example, you might cite a previous study that mentioned your problem as an area where further research needs to be done.
- The length of your introduction will vary depending on the overall length of your synopsis as well as the ultimate length of your eventual paper after you've finished your research. Generally, it will cover the first page or two of your synopsis.
-
2Describe the work done by other researchers in your literature review. Typically, your literature review discusses advancements other researchers have made in the field approaching questions similar to yours. Then, distinguish your research project from those that have already been done to show that you are contributing something new to your field.[5]
- Typically, you should be able to conduct a thorough literature review by discussing 8 to 10 previous studies that are related to your research problem.
- As with the introduction, the length of your literature review will vary depending on the overall length of your synopsis. Generally, it will be about the same length as your introduction.
-
3Set forth the goals or objectives for your research project. Include at least one overall objective that describes the contribution your particular project will make to your field. Then, provide 2 or 3 specific objectives that you hope to accomplish through your project.[6]
- Generally, the overall objective doesn't relate to solving a specific problem or answering a specific question. Rather, it describes how your particular project will advance your field.
- For specific objectives, think in terms of action verbs such as "quantify" or "compare." Here, you're hoping to gain a better understanding of associations between particular variables.
-
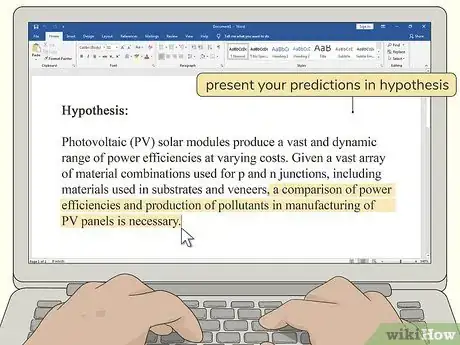
4List your hypotheses for your research project. Your hypotheses represent your predictions of what you will find out as a result of your research. Typically, this involves predicting a relationship between two different variables. Your research project will then attempt to quantify that relationship.[7]
- Specify the sources you used and the reasons you arrived at your hypotheses. Typically, these will come from prior studies that have shown similar relationships.
- For example, suppose a prior study showed that children who were home-schooled were less likely to be in fraternities or sororities in college. You might use that study to back up a hypothesis that home-schooled children are more independent and less likely to need strong friendship support networks.
-
5Discuss the methodology and methods you'll use in your research. The methodology and methods section is the core of your synopsis and lays out for your reader exactly how you're going to answer your research question. Demonstrate to your reader that the study design you've chosen is within your reach and appropriate for answering your research question.[8]
- Expect your methodology to be at least as long as either your introduction or your literature review, if not longer. Include enough detail that your reader can fully understand how you're going to carry out your study.
- This section of your synopsis may include information about how you plan to collect and analyze your data, the overall design of your study, and your sampling methods, if necessary. Include information about the study setting, including the facilities and equipment that are available to you to carry out your study.
-
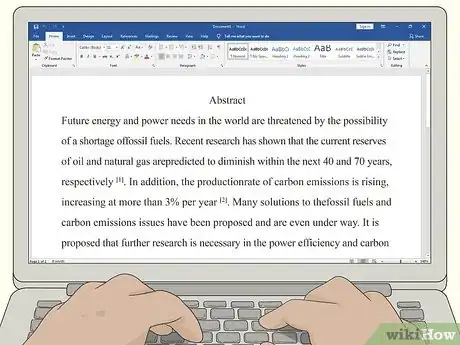
6Complete your abstract last. Since your abstract is a summary of your entire synopsis, it's typically easier to draft this section of your synopsis after you've already finished everything else. That way, you can ensure that your abstract accurately reflects the information provided in your synopsis.[9]
- Use between 100 and 200 words to give your readers a basic understanding of your research project.
- Include a clear statement of the problem, the main goals or objectives of your study, the theories or conceptual framework your research relies upon, and the methods you'll use to reach your goals of objectives.
Tip: Jot down a few notes as you draft your other sections that you can compile for your abstract to keep your writing more efficient.
Finalizing Your Synopsis
-
1Let your synopsis sit for a while before you start editing. You'll have a hard time finding errors or identifying rough passages if you start editing immediately after you finish writing your first draft. Generally, it's best if you're able to put it aside for at least a few days.[10]
- If you don't have that kind of time because you're up against a deadline, at least take a few hours away from your synopsis before you go back to edit it. Do something entirely unrelated to your research, such as take a walk or go to a movie.
-
2Make your writing clear and concise. When you edit your synopsis, get rid of passive-voice constructions in favor of active voice. Use first-person pronouns to describe clearly what you plan to do with your project.
- Eliminate sentences that don't add any new information. Even the longest synopsis is a brief document — make sure every word needs to be there and counts for something.
- Get rid of jargon and terms of art in your field that could be better explained in plain language. Even though your likely readers are people who are well-versed in your field, providing plain language descriptions shows that you know what you're talking about. Using a lot of jargon can seem like you're trying to make yourself sound like you know more than you actually do.
Tip: Free apps, such as Grammarly and Hemingway App, can help you identify grammatical errors as well as areas where your writing could be more clear. However, you shouldn't rely solely on apps since they can miss things.
-
3Check the format of your references. Compare your reference list with your synopsis. If you formatted your reference list before you wrote your synopsis, delete any entries for sources that you ended up not using. If you happened to find a new source that isn't included in your reference list, add the new entry in.[11]
- Reference list formatting is very particular. Reading your references out loud, including the punctuation and spacing, can help you pick up on errors you wouldn't have noticed if you'd just read over it.
- Compare your format to the format in the stylebook you're using and make sure all of your entries are correct.
-
4Proofread your synopsis carefully. You'll typically pick up more errors if you proofread separately from content editing. Once your synopsis reads the way you want it, check spelling and punctuation. Tricks you can use to proofread accurately include:[12]
- Read your synopsis backward by starting on the last word and reading each word separately from the last to the first. This helps you isolate spelling errors. Reading backward sentence by sentence will help you isolate grammatical errors without being distracted by the content.
- Print your synopsis and circle every punctuation mark with a red pen. Then go through them and focus on whether they're correct.
- Read your synopsis out loud, including the punctuation, as though you were dictating the synopsis.
-
5Share your paper with classmates and friends for review. Since you wrote your synopsis, you aren't necessarily the best editor. Classmates or friends can offer a fresh pair of eyes and may pick up on errors that you missed.
- Have at least one person look over your synopsis who isn't familiar with your area of study. If they can understand your project, that tells you that your writing is clear. If there are any parts that confuse them, you know that's an area where you can improve the clarity of your writing.
-
6Do a second round of editing and proofreading. Before you submit your synopsis, give it another thorough read to make sure it's accurate and error-free. Reading aloud will help you catch errors you might have missed in previous rounds of editing.[13]
- If you make significant changes to your synopsis after your first or second round of editing, you may need to proofread again to make sure you didn't introduce any new errors. Don't be surprised if you go through several drafts of your synopsis before it reaches its final form.
References
- ↑ https://admin.umt.edu.pk/Media/Site/iib1/FileManager/FORMAT%20OF%20SYNOPSIS%2012-10-2018.pdf
- ↑ https://eduflair.com/blog/how-to-write-a-synopsis-for-your-research/
- ↑ https://www.scientificstyleandformat.org/Tools/SSF-Citation-Quick-Guide.html
- ↑ https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279917593_Research_synopsis_guidelines
- ↑ http://www.ijdvl.com/article.asp?issn=0378-6323;year=2008;volume=74;issue=6;spage=687;epage=690;aulast=Betkerur
- ↑ https://eduflair.com/blog/how-to-write-a-synopsis-for-your-research/
- ↑ https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279917593_Research_synopsis_guidelines
- ↑ http://www.ijdvl.com/article.asp?issn=0378-6323;year=2008;volume=74;issue=6;spage=687;epage=690;aulast=Betkerur
- ↑ https://www.tesaf.unipd.it/en/sites/tesaf.unipd.it.en/files/ResearchSynopsisWriting_vers.0.pdf