This article was co-authored by Kristi Acuna. Kristi Acuna is a Holistic Nutritionist and the Owner of Holistic Nutrition Center in Orange County, California. With over 15 years of experience, Kristi specializes in a comprehensive and holistic approach to nutrition through nutrition response testing, heart rate variability, thermography, and brainspan. She has experience helping with weight gain, fatigue, insomnia, food allergies, diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome, digestion problems, sinus infections, and PMS and menopause symptoms. Kristi holds a BS in Holistic Nutrition from Clayton College of Natural Health. Holistic Nutrition Center focuses on the root cause of health challenges and helps people heal and restore balance to their bodies.
There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 65,584 times.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin produced by the body in response to sunlight. It aids in the absorption of calcium and helps regulate phosphate levels. Vitamin D deficiency is linked to serious health problems in both children and adults, such as bone weakness, irregular growth and immune deficiencies;[1] however, the symptoms can be hard to detect and might not appear until the condition is serious. Learning about the risk factors and possible symptoms can help you decide if you should request medical testing to confirm a diagnosis of low vitamin D.
Steps
Evaluating Your Risk Factors
-
1Consider your age. Infants and elderly people are at a higher risk. Infants often receive little sun exposure and do not ingest much vitamin D from their diets, especially if they’re breastfed and do not take any supplements. Elderly people require more vitamin D than younger adults and may not spend enough time outdoors due to limited mobility.[2]
- The recommended daily allowance, according to the Institute of Medicine, is 600 IU/day for adults and 800 IU/day for the elderly.[3]
-
2Think of your level of sun exposure. Because the body can synthesize vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, people whose occupations or lifestyles limit their time outdoors, or whose clothing choices keep their skin protected from the sun, may not get enough sun exposure to produce adequate levels of vitamin D.[4]
- People who live in regions with less sunlight are also at a higher risk. These include countries in Northern Europe and Asia, Canada, the Northern United States, Southern Argentina and Chile.
- Children in developed countries, like the United States, tend to spend less time outside, and are more likely to wear sunblock when outside, which inhibits vitamin D synthesis.
Advertisement -
3Take into consideration your skin tone. People with darker skin have higher levels of melanin, which can inhibit the skin's production of vitamin D. For example, in the United States the rate of vitamin D deficiency is higher among African Americans.[5]
-
4Check your weight. Obese people tend to suffer from low vitamin D in greater numbers due to their body’s inability to convert the vitamin into a hormonally active form, no matter how much of it they take in from food or sun exposure.[6]
-
5Consider existing medical conditions. If you suffer from cystic fibrosis, kidney or liver disease, gastrointestinal conditions causing malabsorption such as IBS, Crohn's or celiac disease, you’re at a higher risk for vitamin D deficiency. This is because, due to these conditions, your body might not be able to correctly absorb vitamin D from your food intake.[7]
-
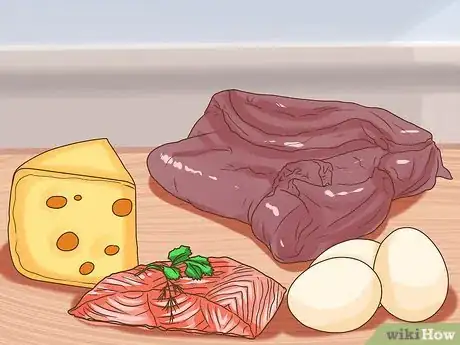
6Be aware of your diet. People can get vitamin D through a limited amount of foods. Eating fatty fish such as salmon, sardines or tuna, eggs yolks, beef liver, some cheeses provides the body with natural sources of vitamin D3, one of its two forms. Vitamin D2 is instead found in grains and supplements.[8]
- Consider vitamin D deficiency testing if you are a vegetarian or vegan, and make sure your diet includes fortified foods such as cereals and orange juice.
Checking Your Body
-
1Spot signs of weakness. Vitamin D deficiency affects your muscle strength. Feeling weak, especially for no particular reason, can be a sign that your vitamin D levels are low.[9]
- In particular, if you have a vitamin D deficiency you might notice that you get sick easily because your immune sickness is weak. You might also have depleted hormone levels and low energy.[10]
-
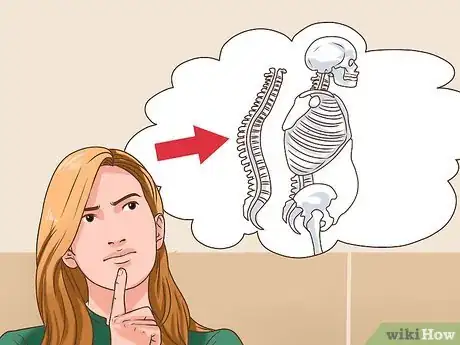
2Check whether you have osteoporosis or bones that break easily. Because vitamin D is necessary for a healthy bone structure, its deficiency can cause malformations in children and a decreased bone density in adults.[11]
-
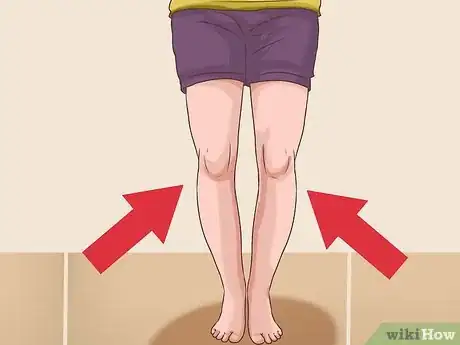
3Look for bowed legs and arms in children. Children who do not get enough vitamin D may show bone deformities and develop rickets. Rickets is the term for the softening of bones that occurs when bone mineralization is defective due to vitamin D, calcium or phosphate deficiencies.[12]
- If left untreated rickets can lead to a curved spine, skeletal deformities, dental problems, and seizures.[13]
- You should talk to your pediatrician if your child is not growing at a consistent rate, and check if this might be due to vitamin D deficiency.
-
4Notice if you experience chronic pain in your bones or difficulty walking. These could be a sign of osteomalacia, a defective bone mineralization in adults linked to low levels of vitamin D.[14]
- Low levels of vitamin D can also be the reason behind pain or a slow recovery after a work out session.
-
5Take note of excessive sweating. This could also be a sign of low vitamin D levels, especially if you sweat in conditions in which your normally wouldn’t, such as mild temperatures or during a period of inactivity.
- Although this might be too vague a symptom for adults, a sweaty forehead in newborns is one of the most evident symptoms of vitamin D deficiency.
-
6Pay attention to any swing in your mood. Low levels of vitamin D can also impact the hormones affecting our mood, such as serotonin. For this reason, some cases of vitamin D deficiency can be misdiagnosed as depression.[15]
Having Your Vitamin D Levels Tested
-
1Consult your doctor. After you’ve checked your symptoms and risk factors, ask your doctor whether these issues might be linked to a vitamin D deficiency. Remember to mention any part of your lifestyle that might be linked to lower levels, such as limited sun exposure or dietary habits.
-
2Ask your doctor for a vitamin D test. This is just a regular blood test in which your blood levels of 25-hydroxy vitamin D is checked. This test, also known as 25(OH)D, is the only way for you to know whether your symptoms are linked to a vitamin D deficiency.[16]
- Healthy individuals usually have a level between 20 ng/ml to 50 ng/ml. A level below 12 ng/mL is a sign of vitamin D deficiency.[17]
-
3Order a vitamin D test online. In the United States, it is possible to take the test without consulting your doctor. Some labs allow you to order a 25(OH)D test online and take it either at home (by piercing your finger and getting a blood sample) or at their closest facilities.
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionI'm taking vitamin D tablets from the doctor. How long does it take to see results?
 Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Family Medicine Physician
-
QuestionWhat if I have severe pain in the knee?
 Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Family Medicine Physician
-
QuestionWhat are the most common symptoms of vitamin D deficiency?
 Kristi AcunaKristi Acuna is a Holistic Nutritionist and the Owner of Holistic Nutrition Center in Orange County, California. With over 15 years of experience, Kristi specializes in a comprehensive and holistic approach to nutrition through nutrition response testing, heart rate variability, thermography, and brainspan. She has experience helping with weight gain, fatigue, insomnia, food allergies, diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome, digestion problems, sinus infections, and PMS and menopause symptoms. Kristi holds a BS in Holistic Nutrition from Clayton College of Natural Health. Holistic Nutrition Center focuses on the root cause of health challenges and helps people heal and restore balance to their bodies.
Kristi AcunaKristi Acuna is a Holistic Nutritionist and the Owner of Holistic Nutrition Center in Orange County, California. With over 15 years of experience, Kristi specializes in a comprehensive and holistic approach to nutrition through nutrition response testing, heart rate variability, thermography, and brainspan. She has experience helping with weight gain, fatigue, insomnia, food allergies, diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome, digestion problems, sinus infections, and PMS and menopause symptoms. Kristi holds a BS in Holistic Nutrition from Clayton College of Natural Health. Holistic Nutrition Center focuses on the root cause of health challenges and helps people heal and restore balance to their bodies.
Holistic Nutritionist
Warnings
- Vitamin D supplements can be beneficial, but you should follow you doctor's advice on the appropriate dose. Like most vitamins, vitamin D can be toxic if people ingest too much at a time.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- If you are high risk for skin cancer, discuss a strategy with your doctor for getting enough vitamin D. Don't overexpose yourself to the sun since other options are available to increase your vitamin D intake.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532266/
- ↑ https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/716434_4
- ↑ https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/#h2
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6075634/
- ↑ https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/716434_4
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6075634/
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15050-vitamin-d--vitamin-d-deficiency
- ↑ https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/vitamin-d/
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/vitaminddeficiency.html
- ↑ Kristi Acuna. Holistic Nutritionist. Expert Interview. 17 September 2020.
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532266/
- ↑ https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/128762-overview
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22459-rickets
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15050-vitamin-d--vitamin-d-deficiency
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15050-vitamin-d--vitamin-d-deficiency
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/vitamin-d-test/
- ↑ https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/tests/25-hydroxy-vitamin-d-test






























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...