wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 33,330 times.
Learn more...
Before you start performing any statistical analysis on the given data, it is important to identify if the data follows normal distribution. If the given data follows normal distribution, you can make use of parametric tests (test of means) for further levels of statistical analysis. If the given data does not follow normal distribution, you would then need to make use of non-parametric tests (test of medians). As we all know, parametric tests are more powerful than non-parametric tests. Hence, checking the normality of the given data becomes all the more important.
Steps
-
1Write the hypothesis. A good way to perform any statistical analysis is to begin by writing the hypothesis. For normality test, the null hypothesis is “Data follows a normal distribution” and alternate hypothesis is “Data does not follow a normal distribution”.
-
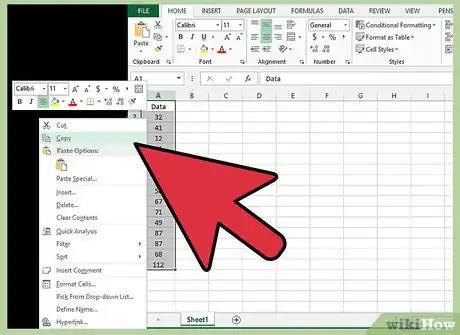
2Choose the data. Select and copy the data from spreadsheet on which you want to perform the normality test.Advertisement
-
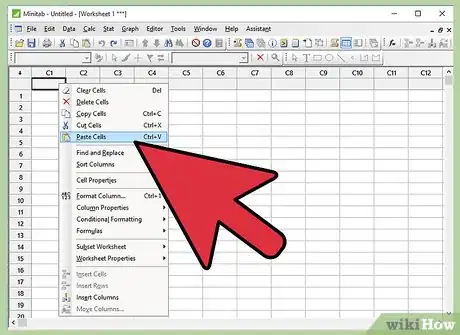
3Paste the data in Minitab worksheet. Open Minitab and paste the data in Minitab worksheet.
-
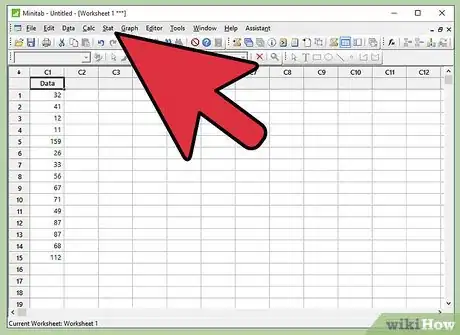
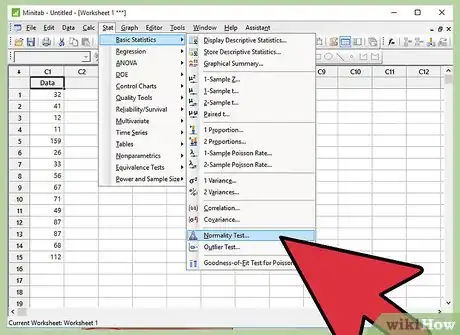
4Click “Stat”. In the menu bar of Minitab, click on Stat.
-
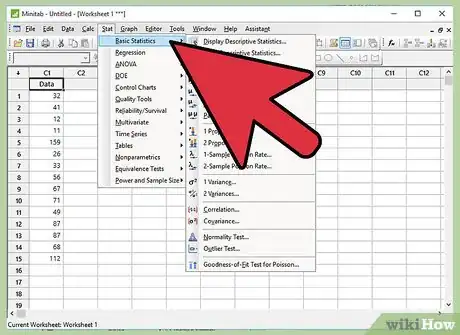
5Click "Basic Statistics".
-
6Click “Normality Test”
-
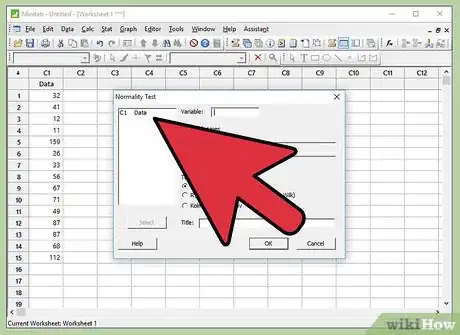
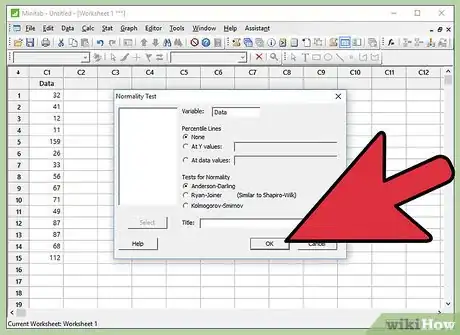
7Select data. A small window named “Normality Test” will pop-up on the screen. Click on the available option inside the white box and then Click “Select”.
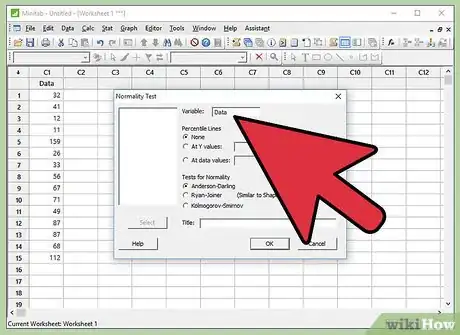
- Be aware that the “Variable” tab will have the name of selected data.
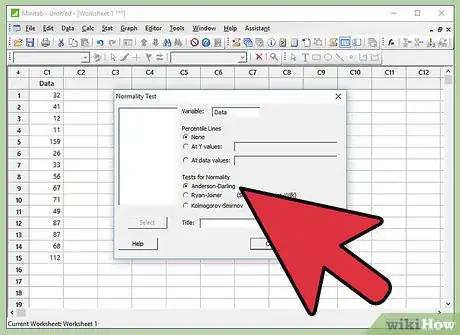
- Also be aware that “Anderson-Darling” is already selected under “Tests for Normality”. Anderson-Darling is the most widely used Normality test. Hence, in Minitab, the default selection of Tests for Normality is “Anderson-Darling”.
-
8Click "Ok".
-
9
-
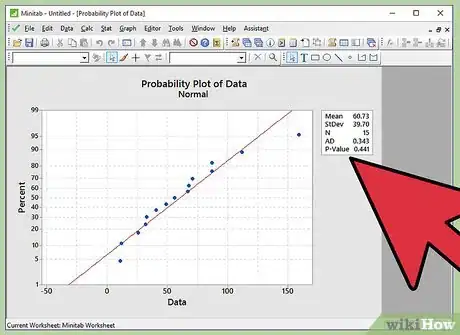
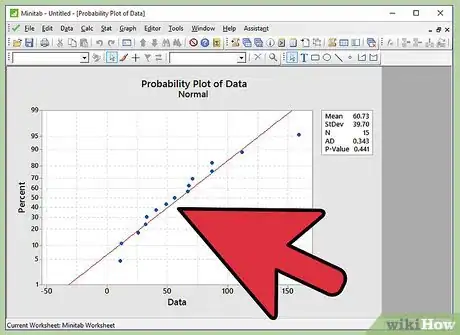
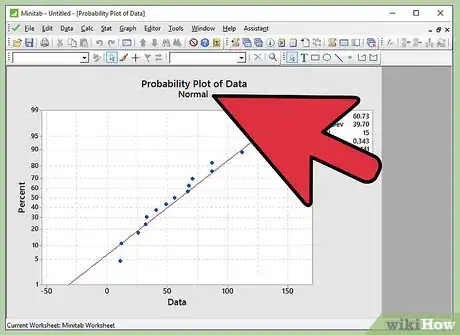
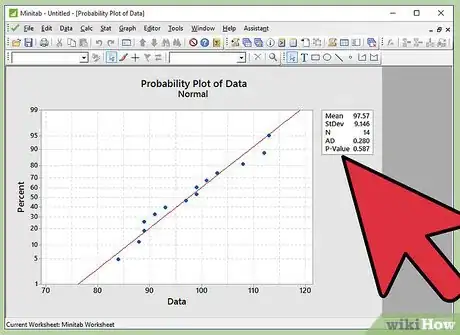
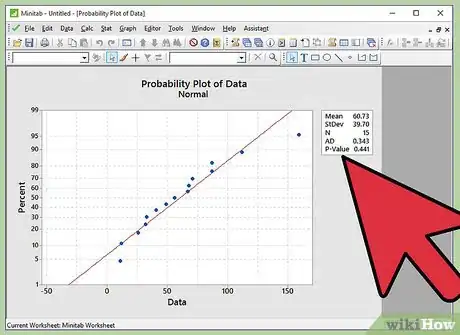
10Infer the results. As described in the step of writing the hypothesis, if we fail to reject the null hypothesis, the inference will be “Data follows a normal distribution”. If we reject the null hypothesis, the inference will be “Data does not follow a normal distribution”. Let’s link the p-value to the written hypothesis.
-
11Do not reject null hypothesis if p-value is greater than 0.05. If the p-value observed in normal probability plot is greater than 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Thus the inference is “Data follows a normal distribution”.
-
12Reject the null hypothesis if p-value is lesser than 0.05. If the p-value observed in normal probability plot is less than 0.05, we reject the null hypothesis. Thus the inference is “Data does not follow a normal distribution”.