wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 9 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
There are 26 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 10,686 times.
Learn more...
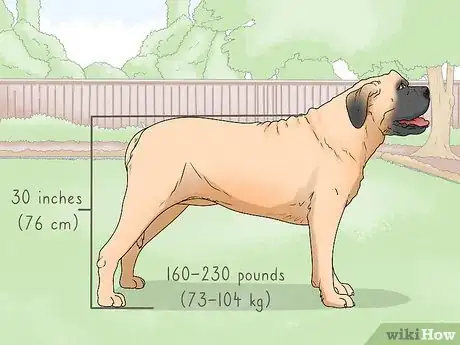
Mastiffs, also called English Mastiffs and British Mastiffs, are among the largest dog breeds,[1] but there's much more than meets the eye when it comes to this breed. There are several other breeds classified as "Mastiffs" also, all of which have their own unique features. This wikiHow will help you distinguish between them and discover whether or not a dog is a Mastiff.
Steps
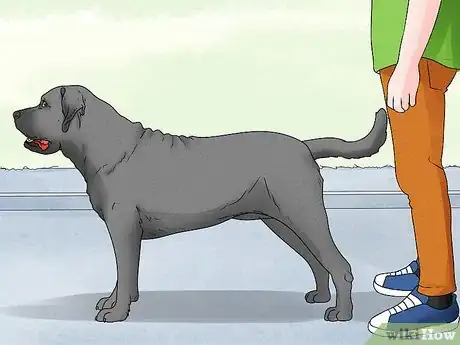
Viewing the Body Structure
Inspecting the Coat
-
1Notice how the coat appears and feels. Mastiffs have moderately short coats. The outer coat is straight and coarse, while the undercoat is dense and close-lying.[15]
-
2Identify the coat color. Look for a fawn or apricot coat, with or without brindle markings, as these are the colors Mastiffs are seen in.[16] A small patch of white on the chest is also possible.[17]
- When a Mastiff is seen with brindle markings, fawn or apricot should be the background color, covered with dark stripes.[18]
-
3
Looking at Temperament
-
1Recognize gentleness. Mastiffs are good-natured and described as "gentle giants". They are gentle and affectionate towards children and are trusted family pets.[21]
-
2See if the dog is calm. Overall, Mastiffs are fairly calm. They are tolerant of other household pets and don't often show signs of aggression.[22]
-
3Check for patience. Another factor that makes Mastiffs great with children is their patience. They typically respond well to human leadership.[23]
-
4Notice if the dog is alert. Mastiffs don't bark constantly, but they may make noise on occasion. This is because they are highly alert dogs, though it is important to train them to only bark when necessary.[24]
-
5Watch for a guarding instinct. Mastiffs desire to protect. They are willing to guard those that look after them and those they are close to.[25]
Identifying Different Mastiff Breeds
There are a few other dog breeds classified as "mastiffs". In general, mastiffs appear to have jowls that overlap the lower lip even as puppies, and they have short yet wide snouts that may lengthen as they get older. They also have triangular ears that are flapped and hang from the side of the face.
-
1Recognize the Neapolitan Mastiff. The Neapolitan Mastiff is a working breed used as a guardian in ancient Roman times.[26] They are very large, with males standing at 26–31 inches (66–79 cm) and weighing 150 pounds (68 kg) and females standing at 24–29 inches (61–74 cm) and weighing 110 pounds (50 kg).[27] They have deep-set eyes that are shades of amber or brown and almost hidden, cropped or uncropped triangular ears, square muzzles with long lips or jowls, and long tails which are wide and thick at the base and tapering towards the tip.[28] Neapolitan Mastiffs have very loose skin, and they appear to have wrinkles all over their massive, stocky bodies, with a strong back and a slow, lumbering gait.[29] Their short, dense, smooth coats are gray/blue, black, mahogany, or tawny in color, with reverse brindle or white markings on the chest, throat, underside, or toes possible.[30] Neapolitan Mastiffs are loyal, watchful, calm, majestic, and powerful.[31]
-
2Identify the Bullmastiff. A result of bulldog and mastiff crosses, Bullmastiffs are another popular mastiff breed.[32] Members of the working group, they are large dogs, standing at 24–27 inches (61–69 cm) in height and weighing 100–130 pounds (45–59 kg).[33] They have medium-sized dark eyes, V-shaped ears that are darker than the coat and medium in size, dark muzzles that are broad and deep, and tails that are strong at the root and tapering at the end and that may be straight or curved.[34] Their bodies are symmetrical, square, and powerfully built but active, with a free, smooth gait.[35] Bullmastiffs have short, dense coats that may be red, fawn, or brindle, with or without a small spot of white on the chest.[36] They are fearless, intelligent, reliable, confident, and docile.[37]
-
3Distinguish the Tibetan Mastiff. Tibetan Mastiffs are ancient guard dogs from Tibet and members of the working group.[38] They are large, standing at least 24 inches (61 cm) tall and weighing 70–150 pounds (32–68 kg).[39] Tibetan Mastiffs have medium-sized almond-shaped eyes that can be any shade of brown, V-shaped drop ears that are medium in size, square muzzles which are broad and well-filled, and well-feathered tails that are carried curled over the back and may be medium to long in size.[40] Their build is athletic and substantial, being well-muscled and strong-boned, and having an athletic and balanced gait.[41] Tibetan Mastiffs have fairly long double coats with straight, hard, coarse fur and a heavy, woolly undercoat, with heavy feathering on the neck and shoulders.[42] Their coats can be black, brown, blue/grey (all three with or without tan markings), or gold, which ranges from light to dark, with potential tan markings on the face, throat, legs, and tail, as well as potential white markings on the chest and feet.[43] Tibetan Mastiffs are reserved, strong-willed, highly intelligent, aloof, and independent.[44]
-
4Know of the Boerboel. Boerboels are members of the working group that were bred to be big-game hunters and protectors.[45] They can weigh anywhere within the 150–200 pounds (68–91 kg) range and stand at 22–27 inches (56–69 cm) in height.[46] They have medium-sized brown eyes, V-shaped ears that are medium in size and hang forward, broad muzzles which narrow slightly toward the nose and include deep jaws, and thick tails that are set fairly high and may be docked.[47] Boerboels have a muscular, blocky, solid build and a powerful, agile gait.[48] They have thick, loose skin and smooth, short, shiny, dense coats that may be brown, red, or fawn of any shade with possible white markings on the legs and forechest, as well as brindle, and black masks are desirable but not always seen.[49] Boerboels are dominant, intelligent, calm, confident, and willing to please.[50]
-
5Spot the Cane Corso. The Cane Corso is a working breed only known in Italy prior to 1988.[51] Cani Corsi are 23.5–27.5 inches (60–70 cm) tall, with a weight proportionate to their height.[52] They have medium-sized almond-shaped eyes that are brown in color (dark brown in dogs with black muzzle and lighter with gray muzzles), cropped or uncropped ears that are triangular and medium in size, very broad muzzles with an almost equal width and length and hanging upper lips, and thick tails without much tapering that may be docked.[53] Cani Corsi are strong, muscular, and athletic in build, with a free-flowing, powerful gait.[54] The coat of a Cane Corso is short, shiny, stiff, and dense, with a light undercoat that thickens in cold weather, and may be black, gray (light or dark), fawn, and red, with or without brindle or white patches on the chest, throat, chin, and toes, fawn and red dogs having a black or gray mask.[55] They are intelligent, majestic, noble, powerful, and affectionate.[56]
-
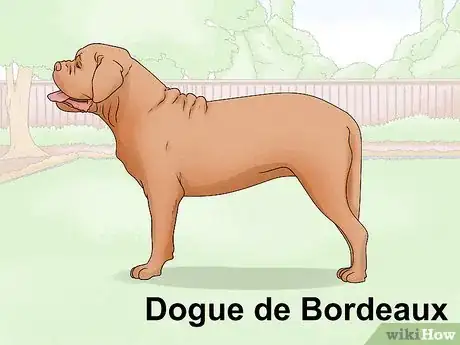
6Distinguish the Dogue de Bordeaux. The Dogue de Bordeaux is a French breed from the working group with a name meaning "Mastiff of Bordeaux".[57] They have a height of 23–27 inches (58–69 cm), males weighing 110 pounds (50 kg) and up and females weighing at least 99 pounds (45 kg).[58] Dogues have hazel-colored eyes that are set wide apart and oval in shape, small ears which are slightly darker than the rest of the coat and fall back, thick muzzles that are broad and short with an undershot bite, and tails which are very thick at the base and curved.[59] They have very muscular bodies, built rather close to the ground, and are stocky and athletic.[60] A Dogue's coat is fine, short, and soft, and might be any shade of fawn, from dark red to light fawn, possibly with white markings on the chest and limbs and may have a black, brown, or no mask (though if no mask is present, it will appear as red).[61] Dogues are courageous, affectionate, calm, vigilant, and balanced.[62]
-
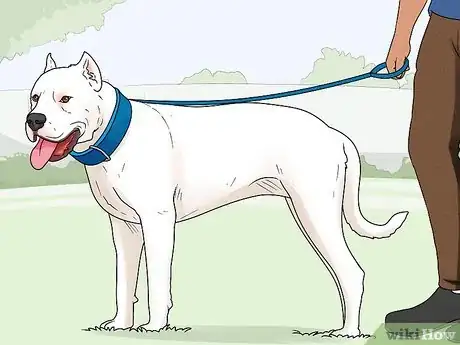
7Know of the Dogo Argentino. The Dogo Argentino is an Argentinian mastiff breed that is part of the working group.[63] Males have a height of 24–26.5 inches (61–67 cm) and weigh 88–100 pounds (40–45 kg), while females stand at 24–25.5 inches (61–65 cm) and weigh 88–95 pounds (40–43 kg).[64] Dogos have medium-sized and almond-shaped eyes, ears that may be erect or natural, strong muzzles with teeth that meet in a scissors or pincher bite, and a tail that starts thick and tapers to the hock.[65] Dogos are athletic, muscular, and balanced in build with a gait of firmness and agility.[66] Their coats are entirely white with the exception of one dark facial spot that may be present and are comprised of straight, smooth, short hair.[67] Dogo Argentinos are courageous, faithful, strong, protective, and tenacious.[68]
-
8Recognize the Great Dane. Great Danes are a working breed that was once used to hunt wild boars.[69] They are one of the largest dog breeds, being 28–32 inches (71–81 cm) tall and weighing 110–175 pounds (50–79 kg).[70] They have dark eyes that are medium in size, high-set ears that are medium-sized and may be cropped or uncropped, deep muzzles with a square jaw, and tails that are broad at the base and tapering and are high-set.[71] A Great Dane's build is powerful, well-formed, and smoothly muscled, with a strong gait of long, easy strides.[72] The coat is thick, short, clean, and glossy, coming in many different colors and patterns, including brindle (with a base color of yellow-gold), fawn, blue, black, harlequin (a white base with black torn patches or merle patches), mantle (black and white with a black blanket), or merle (grey with black torn patches), some patterns allowing masks or white markings.[73] Great Danes are friendly, dependable, spirited, courageous, and never shy or aggressive.[74]
-
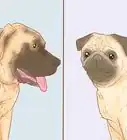
9Identify the Pug. Pugs are a small mastiff-like breed from Ancient China. As a member of the toy group, they are naturally very small, with a height of 10–13 inches (25–33 cm) and a weight of 14–18 pounds (6.4–8.2 kg).[75] Pugs have very large dark eyes that are globular in shape, small ears which are thin and soft and may be of either the "rose" or "button" variety, short and square muzzles with large wrinkles, and tails that are curled as tightly as possible over the hip.[76] They are square, cobby, and have short legs and a long, symmetrical body, along with a free, self-assured, jaunty gait.[77] The coat of a Pug is smooth, fine, short, soft, and glossy, coming in solid black or fawn with a black muzzle, ears, moles, diamond on the forehead, and backtrace,[78] and silver is also, though not-so-commonly, seen.[79] Pugs are even-tempered, playful, outgoing, loving, and stable.[80]
-
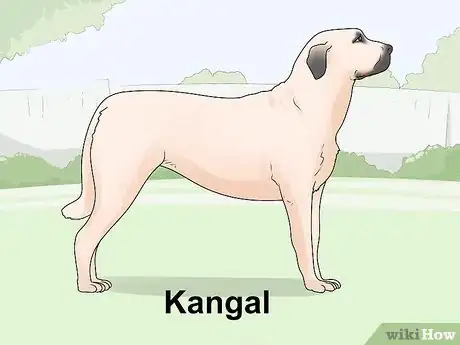
10Know of the Kangal. Kangals, referred to as Anatolian Shepherds by the AKC,[81] are part of the working group and are sometimes used as ranch dogs.[82] Males are 29 inches (74 cm) tall and weigh 110–150 pounds (50–68 kg), while females are 27 inches (69 cm) with a weight of 80–120 pounds (36–54 kg).[83] Kangals have medium-sized eyes which are almond-shaped and range from dark brown to light amber, V-shaped ears that drop to the sides, blocky and strong muzzles with black or brown noses, and rather high-set tails which are long and curled upward.[84] The build of a Kangal is large, rugged, and powerful, well-proportioned and having a powerful yet fluid gait.[85] Kangals may be seen sporting any color or pattern and have short-to-rough fur that is somewhat longer and thicker at the neck, a thick undercoat, and possible feathering on the ears, legs, and tail.[86] They are intelligent, alert, observant, calm, and protective.[87]
Warnings
- Note that Mastiffs may be banned in certain areas because of their potentially intimidating appearance and background.[88] Make sure to be familiar with the breed bans in your area.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/press-releases/the-15-largest-dog-breeds-more-dog-to-love/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/mastiff/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/mastiff/
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Mastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://www.dogtemperament.com/mastiff-temperament/
- ↑ https://www.dogtemperament.com/mastiff-temperament/
- ↑ https://www.dogtemperament.com/mastiff-temperament/
- ↑ https://www.dogtemperament.com/mastiff-temperament/
- ↑ https://www.dogtemperament.com/mastiff-temperament/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/neapolitan-mastiff/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/neapolitan-mastiff/
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/NeapolitanMastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/NeapolitanMastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/NeapolitanMastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/NeapolitanMastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/bullmastiff/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/bullmastiff/
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Bullmastiff.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Bullmastiff.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Bullmastiff.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Bullmastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/tibetan-mastiff/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/tibetan-mastiff/
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/TibetanMastiff.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/TibetanMastiff.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/TibetanMastiff.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/TibetanMastiff.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/TibetanMastiff.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/boerboel/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/boerboel/
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Boerboel.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Boerboel.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Boerboel.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Boerboel.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/cane-corso/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/cane-corso/
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/CaneCorso.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/CaneCorso.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/CaneCorso.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/CaneCorso.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/dogue-de-bordeaux/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/dogue-de-bordeaux/
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/DoguedeBordeaux.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/DoguedeBordeaux.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/DoguedeBordeaux.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/DoguedeBordeaux.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/dogo-argentino/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/dogo-argentino/
- ↑ https://s3.amazonaws.com/cdn-origin-etr.akc.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/26090450/Official-Standard-for-the-Dogo-Argentino-11.12.18-for-website-packet-print-CORRECTED-02.26.19.pdf
- ↑ https://s3.amazonaws.com/cdn-origin-etr.akc.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/26090450/Official-Standard-for-the-Dogo-Argentino-11.12.18-for-website-packet-print-CORRECTED-02.26.19.pdf
- ↑ https://s3.amazonaws.com/cdn-origin-etr.akc.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/26090450/Official-Standard-for-the-Dogo-Argentino-11.12.18-for-website-packet-print-CORRECTED-02.26.19.pdf
- ↑ https://s3.amazonaws.com/cdn-origin-etr.akc.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/26090450/Official-Standard-for-the-Dogo-Argentino-11.12.18-for-website-packet-print-CORRECTED-02.26.19.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/great-dane/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/great-dane/
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/GreatDane.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/GreatDane.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/GreatDane.pdf
- ↑ https://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/GreatDane.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/pug/
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Pug.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Pug.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Pug.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/pug/
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/Pug.pdf
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/anatolian-shepherd-dog/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/anatolian-shepherd-dog/
- ↑ https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/anatolian-shepherd-dog/
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/AnatolianShepherdDog.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/AnatolianShepherdDog.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/AnatolianShepherdDog.pdf
- ↑ http://images.akc.org/pdf/breeds/standards/AnatolianShepherdDog.pdf
- ↑ https://www.yourpurebredpuppy.com/reviews/mastiffs.html