This article was co-authored by Chris M. Matsko, MD. Dr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 13 testimonials and 86% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 844,163 times.
MRSA, short for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, is a particular strain of the staphylococcal (staph) group of bacteria that normally reside on the skin. It is often referred to as a superbug, since it is resistant to methicillin, the antibiotic that kills most staph bacteria. Although it can live on your skin without any problem, if it invades your body via a scratch or cut, it can cause serious infections. These infections often look similar to many other, more benign infections, and without treatment they can become very dangerous. Read on and learn how to identify the symptoms of MRSA.
Recognizing Symptoms
| Area | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Skin |
Breaks in skin, bumps, inflamed areas, rash, necrosis in severe cases |
| Pus |
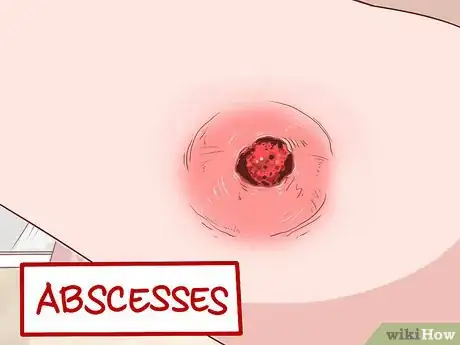
Fluid-filled bumps, boils, abscesses, stye (eyelid) |
| Fever |
Temperatures over 100.4°F, body chills |
| Head | |
| Kidney/Bladder | |
| Lungs |
Coughing or shortness of breath may indicate a spreading infection |
Steps
Identifying Early Symptoms
-
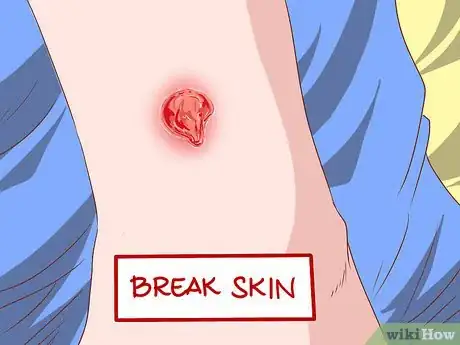
1Look for breaks in the skin. MRSA infections are common where there are cuts or wounds in the skin. Look close to hair follicles. It is also common in hairy areas of the skin, such as the beard area, back of the neck, armpit, groin, legs, scalp, or buttocks.[1]
-
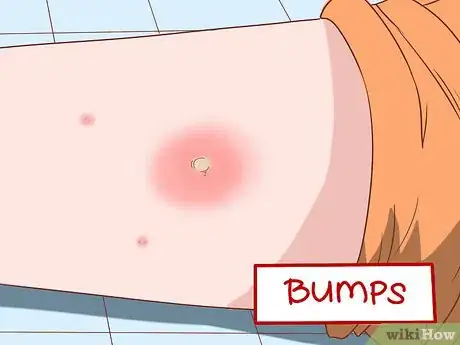
2Watch for bumps or reddened and inflamed skin. MRSA manifests as a bump or sore area on the skin. Many times this can be confused with insect bites, such as spider bites, or it may look like a pimple. Pay attention to any areas of skin that are red, inflamed, painful, or hot to the touch.[2]
- Keep an eye on minor bumps, cuts, scrapes, and redness. If they become infected, see your doctor.[3]
Advertisement -
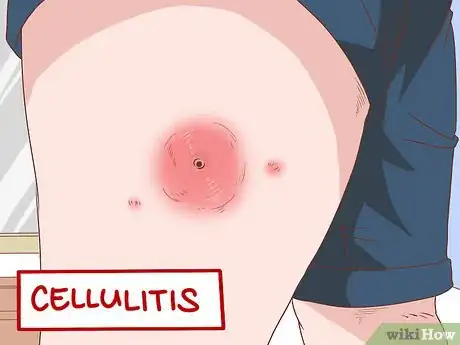
3Look for cellulitis. MRSA can lead to cellulitis, which is an infection of the layers and tissues beneath the skin, which looks like a widespread swollen rash. This causes the skin to look pink or red. The skin may be warm, tender, or swollen.[4]
- Cellulitis can start out as small red bumps. Some areas of the skin may look like a bruise.[5]
-
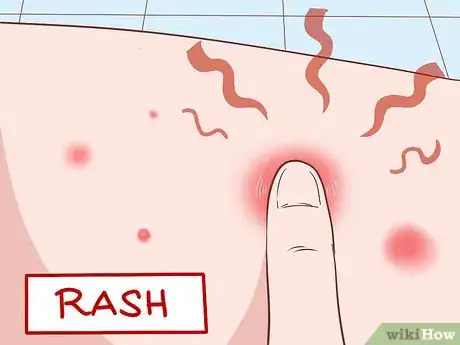
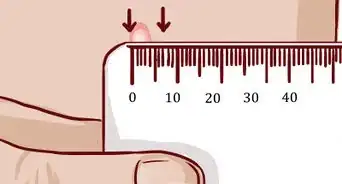
4Be on the lookout for a rash. A rash is reddish colored areas on the skin. If you have widespread red areas, watch it carefully. If it is hot to the touch, spreads quickly, or painful, you may want to see your doctor.[6]
Looking for Pus
-
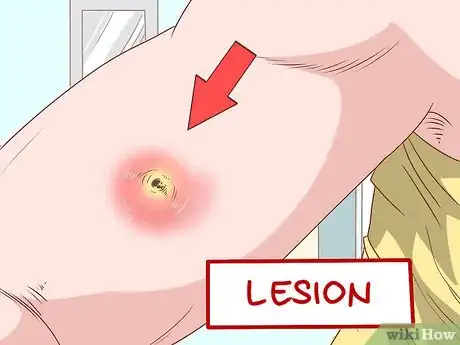
1Decide if the lesion is purulent. If you have a bump or lesion, look for a fluid filled cavity that is movable and compressible. Look for a yellow or white center with a head. There might also be draining pus.[7]
-
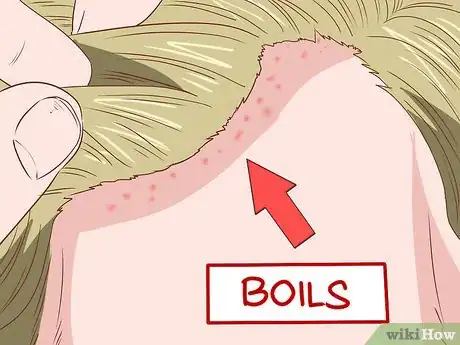
2Look for boils. Boils are pus-filled infections of the hair follicles. Check in your scalp for bumps. Also check any other places with hair, like your groin, neck, and armpit.[8]
-
3
-
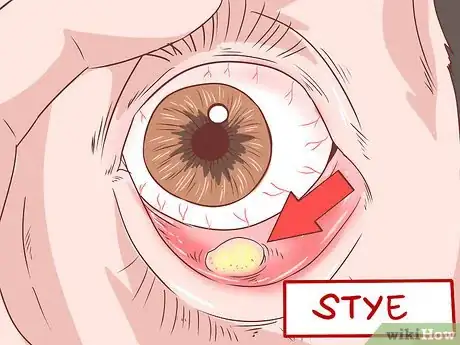
4Be wary of a stye. A stye is an infection of the oil glands of the eyelid. This causes inflammation and redness on the eye and eyelid. The stye can be internal or external. The lump will usually have a whitish or yellowish head that looks like a pimple.[11] It may hurt to blink.
-
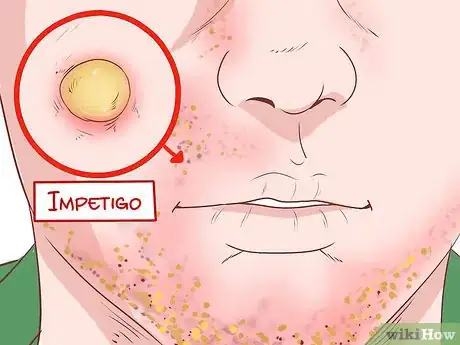
5Watch out for impetigo. Impetigo is a pus blister on the skin. These pus blisters can be large in size. They may burst and leave a honey-colored crust around the infected area.[12]
Handling a Severe Case
-
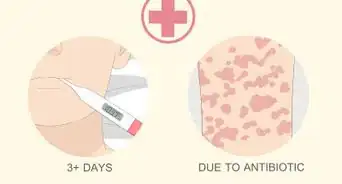
1Track your improvement. If your doctor has diagnosed you with staph infection and given you antibiotics, your condition should improve within two to three days. If you do not see any improvement, there is a chance that you have MRSA. Once you are colonized with MRSA it is likely that you can become reinfected more easily. [13] Keep an eye on your condition, and be prepared to return to your doctor on short notice.
-
2Watch out for headaches, fever, and fatigue. Any of these symptoms might indicate a serious infection when coupled with a staph or MRSA diagnosis.[14] The combination may feel similar to flu symptoms. You may also experience some dizziness and confusion.
-
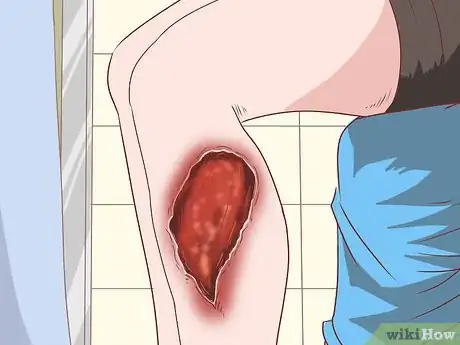
3Notice the signs of a deeper MRSA infection. As the infection spreads through your body, it can choke the lungs; inflame your urinary tract; and even begin to eat your flesh. Untreated MRSA can result in necrotizing fasciitis, a rare but horrific flesh-eating disease.
- Notice the signs that MRSA has spread to the lungs. If the infection is still undetected and left untreated, there is a risk that it can spread to the lungs. Look out for coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.[17]
- A high fever and body chills, possibly accompanied by urinary tract infection, are signs that the MRSA has spread to other organs of the body, such as the kidneys and urinary tract.
- Necrotizing fasciitis is very rare, but not unheard-of. This may manifest as a severe pain in the infected area.
-
4Seek treatment immediately. If you think that you're infected with any stage of MRSA, act as quickly as possible before the bacteria eats its way any deeper into your system. Even if you aren't sure: ask a doctor. MRSA can be a serious and life-threatening condition, and it isn't worth it to take any chances.[18]
- Treatment for community-acquired MRSA is Bactrim and if you are hospitalized it is IV vancomycin.
Expert Q&A
-
QuestionI have had MRSA twice. How do I know if bumps under my armpit are MRSA?
 Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Family Medicine Physician You have to be very careful if you have already been colonized with MRSA. You cannot be sure just by looking at the bumps if they are MRSA or not. You have to get a tissue sample/culture. Usually bumps are pus filled and erythematous, which are more likely to be MRSA.
You have to be very careful if you have already been colonized with MRSA. You cannot be sure just by looking at the bumps if they are MRSA or not. You have to get a tissue sample/culture. Usually bumps are pus filled and erythematous, which are more likely to be MRSA. -
QuestionIs MRSA usually treatable when diagnosed? Will it always prevent a person from working?
 Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Family Medicine Physician MRSA is very treatable. Treatment for community acquired MRSA is Bactrim. You should practice good hygiene, and stay away from infants and small children. Unless you are a healthcare worker, it should not prevent you from working.
MRSA is very treatable. Treatment for community acquired MRSA is Bactrim. You should practice good hygiene, and stay away from infants and small children. Unless you are a healthcare worker, it should not prevent you from working.
Warnings
- If you have a compromised immune system, you are at greater risk of suffering from the more severe symptoms of MRSA, and the infection is more likely to prove fatal.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- MRSA is too hard for you to identify on your own. If you suspect you have any of these symptoms, call a doctor. The doctor will carry out the diagnostic tests to decide whether or not you have the disease.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- If you have abscesses, boils, or other suspicious skin marks, don't poke at it or try to "pop" it.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/communicable/athletic_skin_infections/bacterial.htm
- ↑ http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/10634.php#signs_and_symptoms
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/mrsa/basics/symptoms/con-20024479
- ↑ http://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/ss/slideshow-closer-look-at-mrsa
- ↑ http://www.medicinenet.com/mrsa_infection/page4.htm#what_are_the_signs_and_symptoms_of_a_mrsa_infection
- ↑ http://www.medicinenet.com/mrsa_infection/page4.htm#what_are_the_signs_and_symptoms_of_a_mrsa_infection
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/mrsa/pdf/MRSA_ProviderBrochureF.pdf
- ↑ http://www.medicinenet.com/mrsa_infection/page4.htm#what_are_the_signs_and_symptoms_of_a_mrsa_infection
- ↑ http://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/ss/slideshow-closer-look-at-mrsa
- ↑ http://www.emedicinehealth.com/mrsa_infection/page5_em.htm#mrsa_infection_symptoms_and_signs
- ↑ http://www.emedicinehealth.com/sty/article_em.htm
- ↑ http://www.emedicinehealth.com/impetigo/article_em.htm
- ↑ http://www.skinsight.com/diseaseGroups/mrsa.htm
- ↑ http://www.mass.gov/eohhs/gov/departments/dph/programs/id/epidemiology/providers/mrsa/methicillin-resistant-staphylococcus-aureus-mrsa.html#4
- ↑ https://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/communicable/athletic_skin_infections/bacterial.htm
- ↑ http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/10634.php#signs_and_symptoms
- ↑ http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/10634.php#signs_and_symptoms
- ↑ http://www.mrsasurvivors.org/about/mrsa-sepsis
About This Article
To identify symptoms of MRSA, look for breaks in the skin, as well as bumps or reddened and inflamed skin. Additionally, note if the skin is warm, tender, swollen, or breaks out in a red rash. You should also be aware of any fluid filled cavities as these can be signs of MRSA. If you suspect you have MRSA, seek medical attention immediately before the bacteria spreads deeper into your system. To learn how to recognize the signs of a deeper MRSA infection, keep reading!











-Step-11.webp)












































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...