This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff. Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards.
There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 31,035 times.
Learn more...
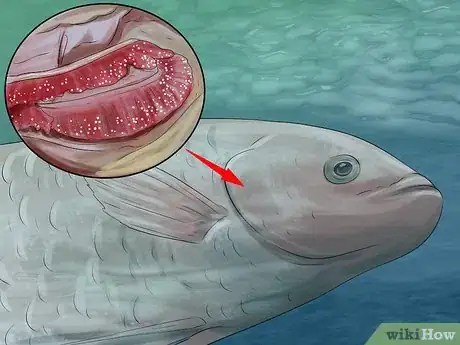
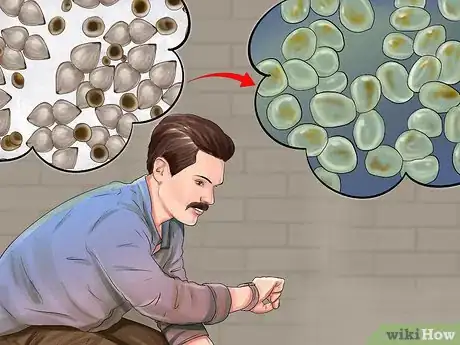
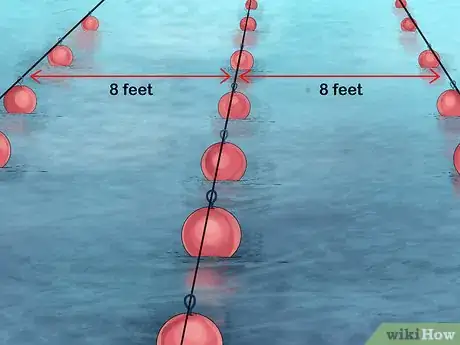
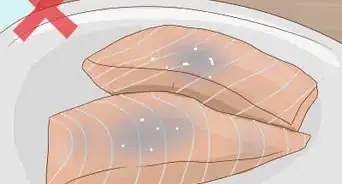
Farming freshwater mussels can be really rewarding process. It involves pairing mussel embryos with a host species of fish until they grow large enough to survive on their own. In deeper waters, fishermen may use special ropes to gather microscopic mussel spawn and allow them to grow undisturbed for a more bountiful harvest. Regardless of how it's done, raising freshwater mussels requires quite a bit of specialized knowledge and equipment, so you may need to enlist the help of professionals for this task.
Steps
Warnings
- Never release mature mussels farmed in tanks into local bodies of water without proper authorization and assistance. Doing so could be disruptive to the natural ecosystem in your area.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You’ll Need
- Freshwater tank or pen
- Host fish specimens
- Phytoplankton or algae (for supplementing diet)
- Fishing boat
- Mussel rope
- Buoys
- Steel cable
- Tow line or hand hook
- De-clumping machine (optional)
References
- ↑ https://www.dgif.virginia.gov/wildlife/freshwater-mussels/
- ↑ https://www.dgif.virginia.gov/wildlife/freshwater-mussels/
- ↑ https://s3.amazonaws.com/delawareestuary/Standard+Methods+Bank+Documents/PDE-FMRP-Method-10+Glochidia+Extraction+and+Assessment.pdf
- ↑ https://www.dgif.virginia.gov/wildlife/freshwater-mussels/
- ↑ https://www.dgif.virginia.gov/wildlife/freshwater-mussels/
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=URHTrAAkpr0&feature=youtu.be&t=145
- ↑ https://www.in.gov/dnr/fishwild/8684.htm
- ↑ https://www.independent.co.uk/environment/nature/growing-mussels-precious-freshwater-shellfish-are-thriving-in-a-unique-green-project-10000858.html
- ↑ http://www.uvm.edu/~pass/tignor/mussels/growth.htm
- ↑ https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40071-015-0098-6
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=16WGcA7U0VY&feature=youtu.be&t=84
- ↑ http://godeepaquaculture.com/mussels/growing-methods/
- ↑ http://godeepaquaculture.com/mussels/growing-methods/
- ↑ https://thefishsite.com/articles/production-methods-for-the-mediterranean-mussel
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=16WGcA7U0VY&feature=youtu.be&t=59
- ↑ https://www.nsf.gov/discoveries/disc_summ.jsp?cntn_id=132832
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PqY3MCMDxlM&feature=youtu.be&t=142
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2_HEMacNFbI&feature=youtu.be&t=209