wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 12 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 129,018 times.
Learn more...
Have you ever had to look up a value in a table only to find that the conditions you have are found in between those that are listed? What did you do when this happened? You probably just rounded off. An alternative way is to interpolate. This is a more accurate way of getting the desired value proportionally from a table when the conditions are not listed (see the "Warning" section below).
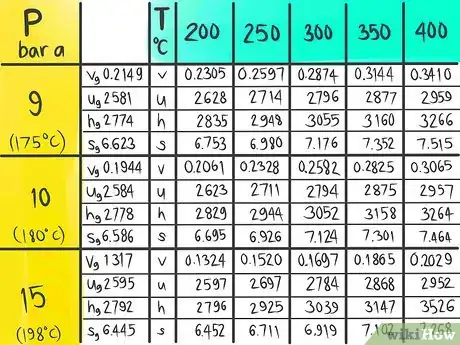
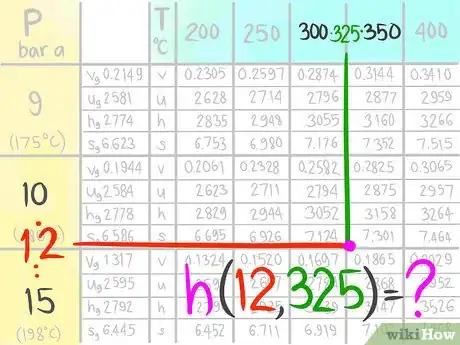
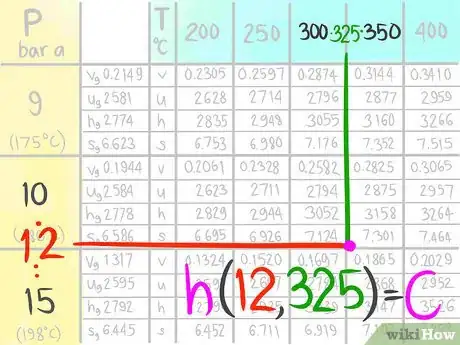
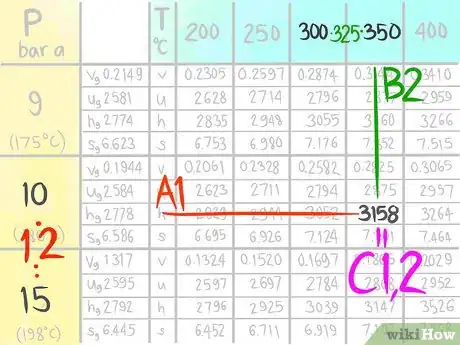
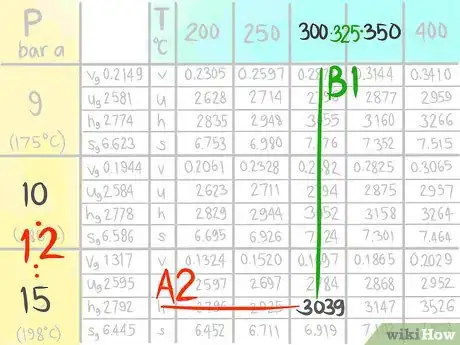
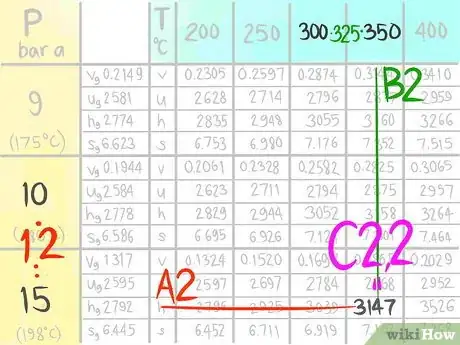
A steam table (which lists Temperature and Pressure conditions to give Enthalpy, Entropy, Specific Volume and Specific Internal Energy values) is an example of a table that may need interpolation. The following instructions will teach you how to do a double linear interpolation. For this demonstration, use the steam table to find the Enthalpy (h) at the conditions 12 bar a, which is designated as A, and 325 C, which is called B in this article.
enthalpy the measure of the heat content as a relation in a system as in chemical analysis by heating and then recording the temperature of a phase change, for example: when it changes from a solid to liquid or to a gas to help identify a substance.
Steps
-
1Click on the image of the example steam table to open that image in a new window in a larger size to be easier to see it clearly.
-
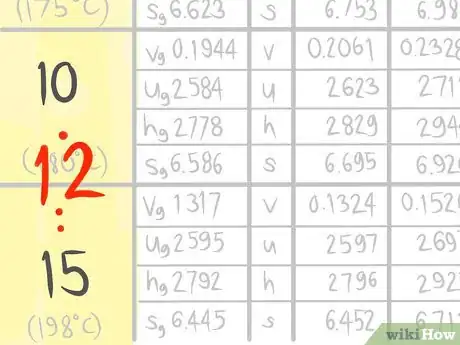
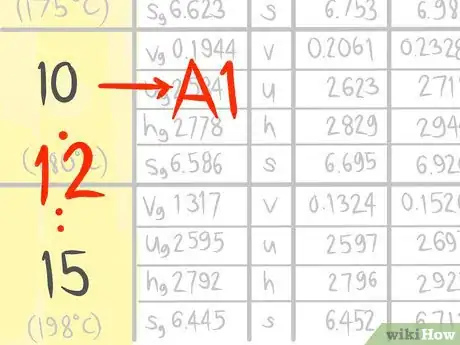
2Locate where 12 bar a (A) would be.Advertisement
-
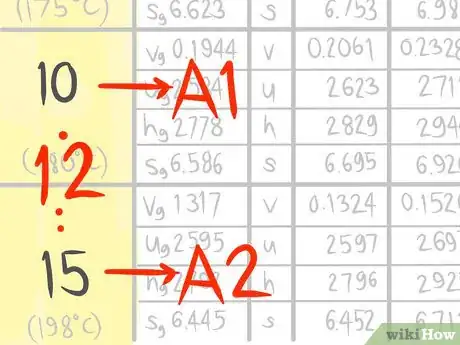
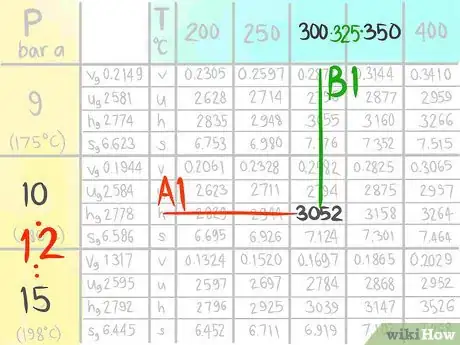
3Call the value that comes before A1.
-
4Call the value that comes after A2.
-
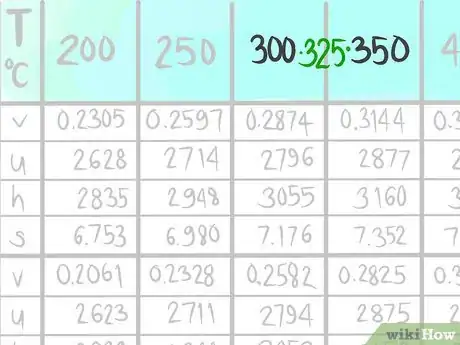
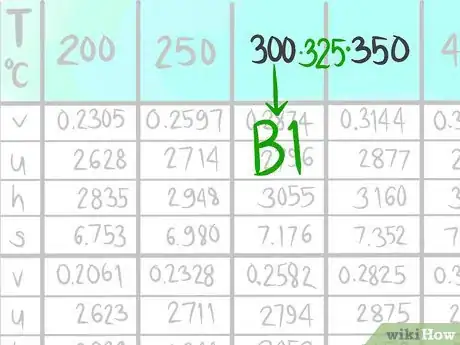
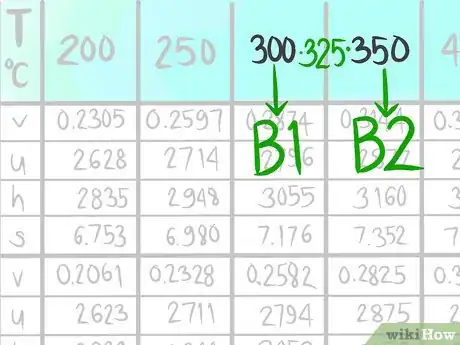
5Locate where 325 C (B) would be.
-
6Call the value that comes before B1.
-
7Call the value that comes after B2.
-
8Locate where the enthalpy value would be at 12 bar a and 325 C.
-
9Call this enthalpy value C.
-
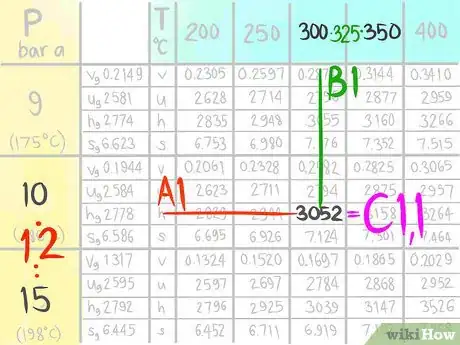
10Locate the value at (A1,B1).
-
11Call the value C1,1.
-
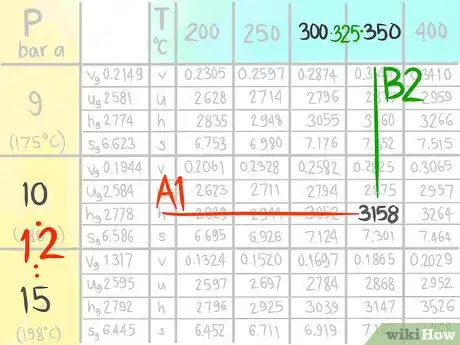
12Locate the value at (A1,B2).
-
13Call the value C1,2.
-
14Locate the value at (A2,B1).
-
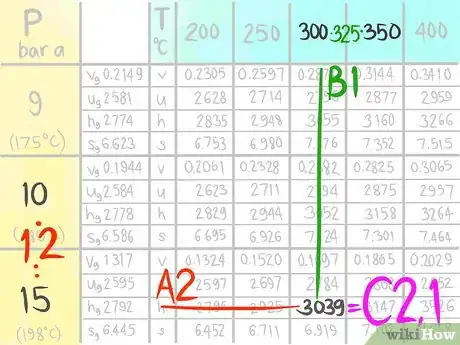
15Call the value C2,1.
-
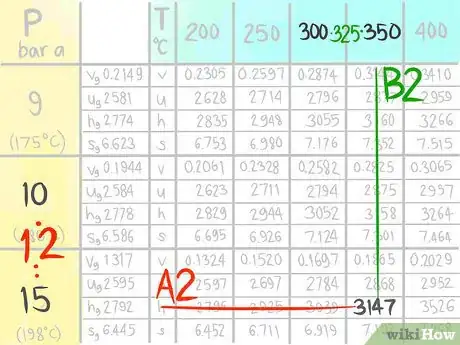
16Locate the value at (A2,B2).
-
17Call the value C2,2.
-
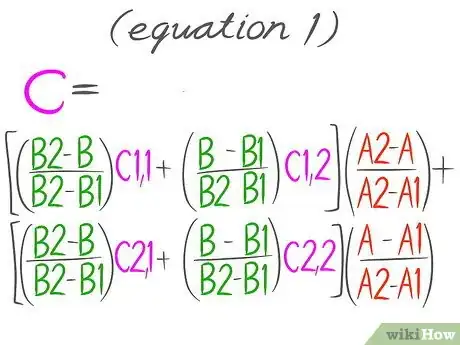
18This is the Equation 1.
-
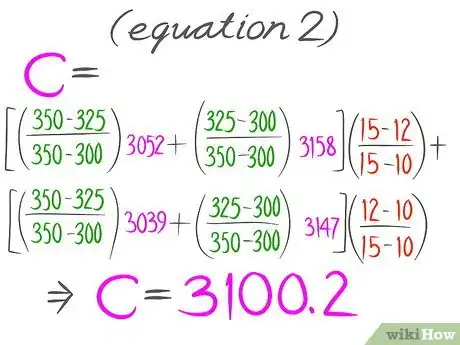
19Plug values in Equation 1. It should then look like Equation 2 with values in place of the variables.
Warnings
- Huge jumps between listed values indicate a phase change, if the current readings are true. When this happens, interpolating will not give an accurate value.⧼thumbs_response⧽