This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff. Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards.
There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 250,007 times.
Learn more...
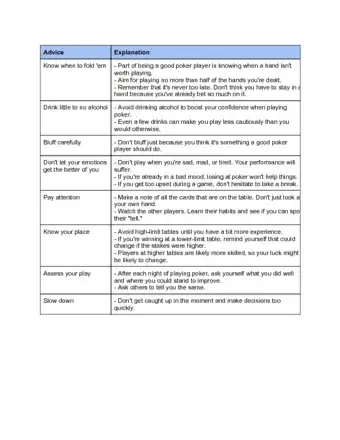
Bluffing in poker is a risky strategy that can pay off in a satisfying way. Beginning poker players often think bluffing should happen often, but it's best to be selective about when you bluff. Practice bluffing when the stakes are low to build your skill in convincing opponents that you have a good hand. Choose your timing carefully, then slowly raise the bet over the course of the hand to pressure the other players to fold. You won't always be successful, but by understanding the best circumstances and timing of bluffing, you can increase your odds of bluffing to win a hand.
Steps
Choosing When to Bluff
-
1Limit your bluffs as much as possible. Beginners tend to think that bluffing is a bigger part of poker than it actually is. However, bluffing is actually a strategy that you should rarely use. You should be relatively sure that you can get your opponents to fold before going into a bluff.[1]
- Never bluff just because you haven’t bluffed in a while and think you should.
-
2Bluff when the stakes aren’t too high if you are a beginner. Although it can be tempting to bluff your way to big winnings, it’s a more effective strategy to bluff when the stakes are lower. Not only are you more likely to get your opponent to fold, you won’t lose as much if your bluff is called.[2]
- Smaller bets are more convincing to the other players.
Advertisement -
3Bluff strong players rather than weak ones. Newbies and players who don’t have a strong understanding of poker will be more likely to continue betting on their own hand, no matter what. They tend to not take their opponents’ hands into account at all. A very weak player probably won’t fold.[3]
- A good player will try to assess the strength of your hand to determine if you are bluffing. A weak player will not notice.
-
4Begin bluffing pre-flop. If you are in last position and the players to your left have been fairly tight, begin to bluff. Put pressure on the other players by putting in a raise. Some will fold before the flop.[4]
- Starting to bluff pre-flop gives you the advantage of looking at immediate reactions of your opponents and leaving you plenty of time to reassess your strategy before the end of the hand.
-
5Bluff post-flop if you are in a late or last position. Watch your opponents’ reactions and bets in order to determine if they have a strong hand and pressure them into folding. Make sure your reaction to the flop matches the story you want your opponents to believe about the hand you have.[5]
- You have the advantage to bluff from a late position, especially if it seems like your opponents are looking for a way to get out of the hand.[6]
-
6Quit when it becomes clear your opponent isn’t convinced. You should only follow through on a bluff if you are sure you can convince your opponent to fold. Otherwise, there is no use throwing more money into the pot. Get out of the hand if your opponent seems confident that they can beat you.[7]
- Remember that you can’t win a bluff if the game goes to a showdown. Don’t be embarrassed to be caught in a bluff. It’s better than losing more money by having your bluff called.
Convincing Your Opponents
-
1Try to bluff one player at a time. It is much more effective to bluff one other person. It is unlikely that you will be able to get more than 2 players to fold by bluffing, no matter how convincing you are.[8]
- The more players there are in the game, the more likely it is that one of them will call your bluff.
-
2Build your table image throughout the game. Create an image for yourself so that your opponents will know what kind of player you are. For example, if you build up a history of betting tightly and staying calm, simply keeping up the same actions while bluffing will help convince your opponent that you have a strong hand.[9]
- Tight bets are seen as stronger. If you are a loose player, your opponent won’t know what to expect from you and is more likely to call your bluff.
-
3Stay calm, or give the appearance of being calm. Signals like being defensive with your poker chips, betting too quickly, calling bets rather than raising them, and either avoiding eye contact or making intense eye contact can all show nervousness to your opponents. Try to keep quiet to avoid being overly defensive, use relaxed movements, and smile genuinely to convince the other players that you have a strong hand.[10]
- If you don't think you can act convincingly, try to be still and fly under the radar. Tells are very difficult to spot accurately, but overcorrecting nervousness will signal to other players right away that you are bluffing.
-
4Raise the bet, but not too much. Your bet should fit in with the betting history of the table. If you suddenly go all in on a hand that you haven’t been betting aggressively on, your opponent is more likely to think you are bluffing. Instead, raise your bets gradually over the course of the hand.[11]
- Raising the stakes earlier in the hand is more likely to scare other players away, making for a successful bluff.
-
5Control your own tells. Bluffing is lying, so if you know you react a certain way when you lie, try to control that reaction. One of the most common tells is freezing up and becoming quiet. Try to stay relaxed and your actions similar to how they have been the rest of the game.[12]
- Keep your movements loose and relaxed to convince your opponents.
- Don’t talk too much, especially if you aren’t confident in your ability to lie convincingly.
Trying Different Kinds of Bluffs
-
1Make a quick bluff for lower risk and lower payoff. Most bluffs in poker are quick bluffs. These happen when the stakes are small- or medium-sized pots and the other players don't seem that interested in winning. In a successful quick bluff, raise the bet and everyone else will fold.[13]
- Try not to overuse quick bluffs, or your opponents will come to anticipate them from you.
-
2Go all-in at the river. To force a decision from the remaining players, go all in at the end of the game, at the river. This is a confident move at the end of the hand, and your opponent will be forced to either fold or go to a showdown.[14]
- Although this bold strategy has the potential to pay off, you also have to be prepared to lose everything.
-
3Increase your odds by semi-bluffing. Semi-bluffing refers to a situation in which you have an okay hand that could possibly improve after the flop or the turn. This is still considered bluffing because even if you are confident your hand will improve, you technically can’t win with the cards in your hand. However, the goal is still to use your confidence to cause the other players to fold.[15]
- A semi-bluff is a good strategy because there are two possible routes to winning the hand.
-
4Use a pure bluff as a last resort. A pure bluff would happen if you reach the end of the river with nothing in your hand and no other options besides bluffing or folding. You can place a bet and hope your opponent folds in order to win.[16]
- This should be used as a last resort because if your opponent calls your bluff, you will almost always lose.
- These are also known as stone cold, total, or naked bluffs.
Warnings
- Never play out of your bankroll. When you play higher limits with a great chance of losing all of your poker money quickly, you would be playing "out of your bankroll." If you don't have enough to bankroll "300" buy-ins for Limit Hold'em games/tournaments, then you are out of your bankroll.[17] Notice that means you would risk less than 1/2% of you available money; so, playing remains a game not an act of desperation. Don't go for broke. Work up to where you can afford your ventures.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Never play too loose. Playing really tight might mean only playing when you have pairs, from 6s up to As, and playing ace-high hands AK down to AJ, betting only within those limits.[18]⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You'll Need
- Playing cards
- Poker chips
- Bankroll management (real or play money) for the kind of game/tournament
References
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pq2I4Xyk-Nc&feature=emb_logo
- ↑ https://www.pokernews.com/strategy/seven-considerations-when-bluffing-or-when-facing-a-bluff-29616.htm
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pq2I4Xyk-Nc&feature=emb_logo
- ↑ https://www.cardschat.com/bluffing.php#times
- ↑ https://www.cardschat.com/bluffing.php#times
- ↑ http://www.pokerology.com/lessons/bluffing-in-poker/
- ↑ https://www.cardschat.com/bluffing.php#quit
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pq2I4Xyk-Nc&feature=emb_logo
- ↑ https://www.cardschat.com/bluffing.php#image
- ↑ https://www.cardschat.com/poker-tells.php
- ↑ http://www.pokerology.com/lessons/bluffing-in-poker/
- ↑ https://www.cardschat.com/poker-tells.php
- ↑ https://www.pokerlistings.com/strategy/how-not-to-suck-at-poker-stop-bluffing
- ↑ https://upswingpoker.com/overbet-all-in-river-bluff-strategy/
- ↑ https://www.cardschat.com/bluffing.php#semi-bluff
- ↑ https://www.pokerlistings.com/strategy/how-not-to-suck-at-poker-stop-bluffing
- ↑ Basic Bankroll-management
- ↑ http://themoth.org/posts/stories/the-big-things-you-dont-do Page-down to list of cards that helped her get started, Annie Duke, on TheMoth.ORG, as heard on NPR, "The Big Things You Don’t Do" (Winner: 2004 World Series of Poker Tournament of Champions and National Heads-Up Poker Championship 2010)